The Sun is the closest star to Earth. Stars are the only ones in the Universe capable of emitting light. The Sun is our primary energy source, which manifests itself with light and huge amounts of heat. It exerts a strong gravitational attraction on the planets, making them spin around the Sun. The Sun (and the entire Solar System) rotates around the center of the Milky Way, our
How big is the Sun?
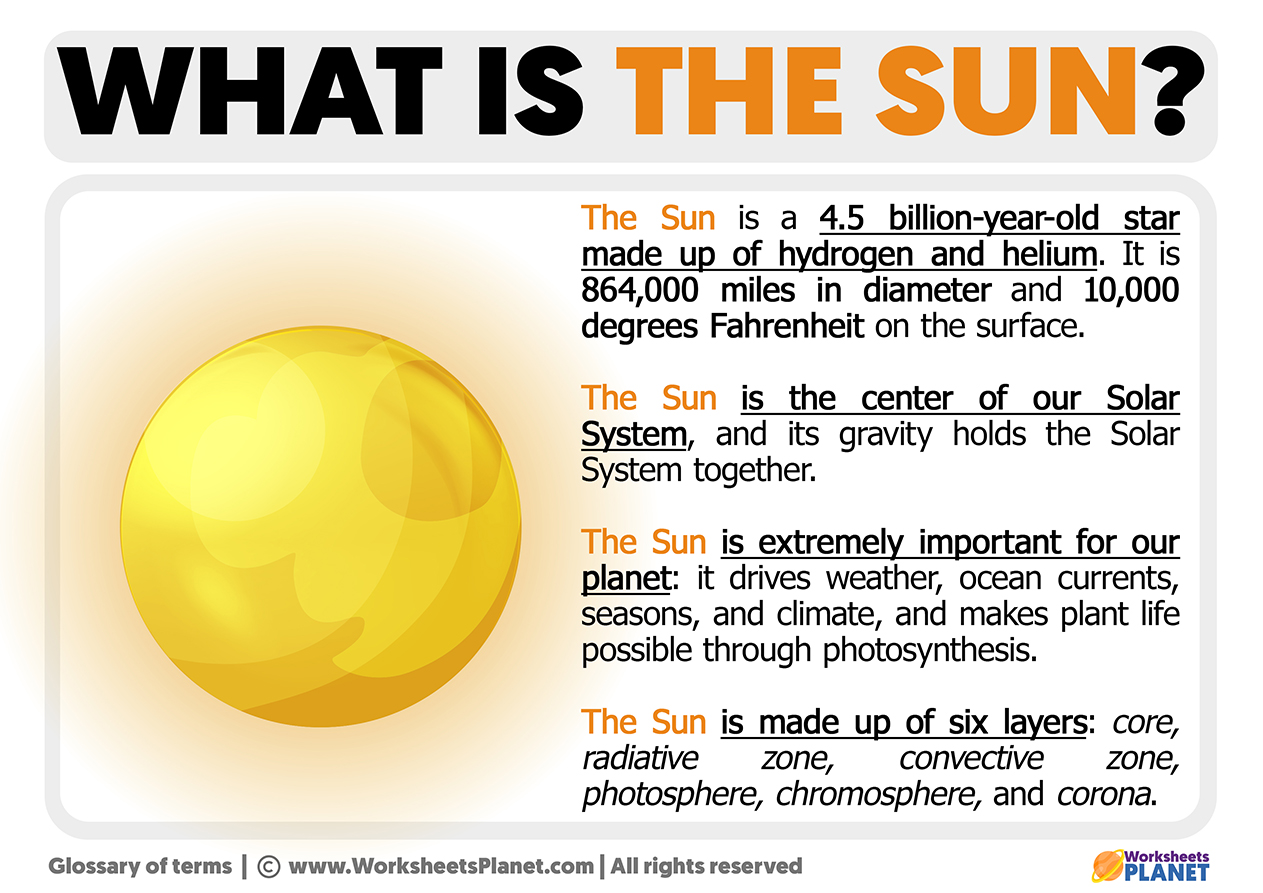
Its diameter is 109 times bigger than Earth’s diameter; it is 864,000 miles in diameter. The Sun could hold more than a million Earth planets inside it.
What is the temperature of the Sun?
We only can see the outer layer of the Sun, which is called the Photosphere and has a temperature that reaches 5,500 degrees Celsius on the surface and more than 15 million degrees Celsius at the core.
The Sun formed 4.5 billion years ago. It has already used almost half of the hydrogen in its core so it will run out in about 5 billion years. Then it will get bigger and bigger, reaching nearly a hundred times its current size. It will burn like a red giant for another billion years, then explode into a white dwarf.
Parts of the Sun
The structure of the Sun can be imagined as a ball that can be divided into several concentric layers.
- Core: here is where nuclear fusion occurs due to high temperature. It is the generator of the Sun’s energy and reaches 15 million degrees.
- Radiative Zone or radiation zone: the particles that carry energy (photons) try to escape abroad, but this attempt can last about a hundred thousand years because these photons are continuously absorbed and sent in other directions than the one they had.
- Convective Zone: in this zone, convection occurs. Columns of hot gas rise to the surface at speeds exceeding 200 miles, then cool and descend again.
- Photosphere: it is a thin outer layer of approximately 300 km. It is the part of the Sun that we see, the surface. Dark spots appear in the Photosphere, preserving a temperature of about 5,500 degrees Celsius.
- Chromosphere: is reddish, with a very low density and a very high temperature, more than half a million degrees.
- Corona: The corona is the outer shape of the Sun’s atmosphere. It has a large extension, high temperatures, and very low density. The corona is made up of rarefied gases and enormous magnetic fields that constantly vary their form. The corona can only be seen during total eclipses of the Sun.

