The ozone layer is a thin portion of the Earth’s atmosphere that absorbs almost all of the sun’s damaging ultraviolet rays. The ozone layer is about 15-30km above the Earth’s surface in the stratosphere.
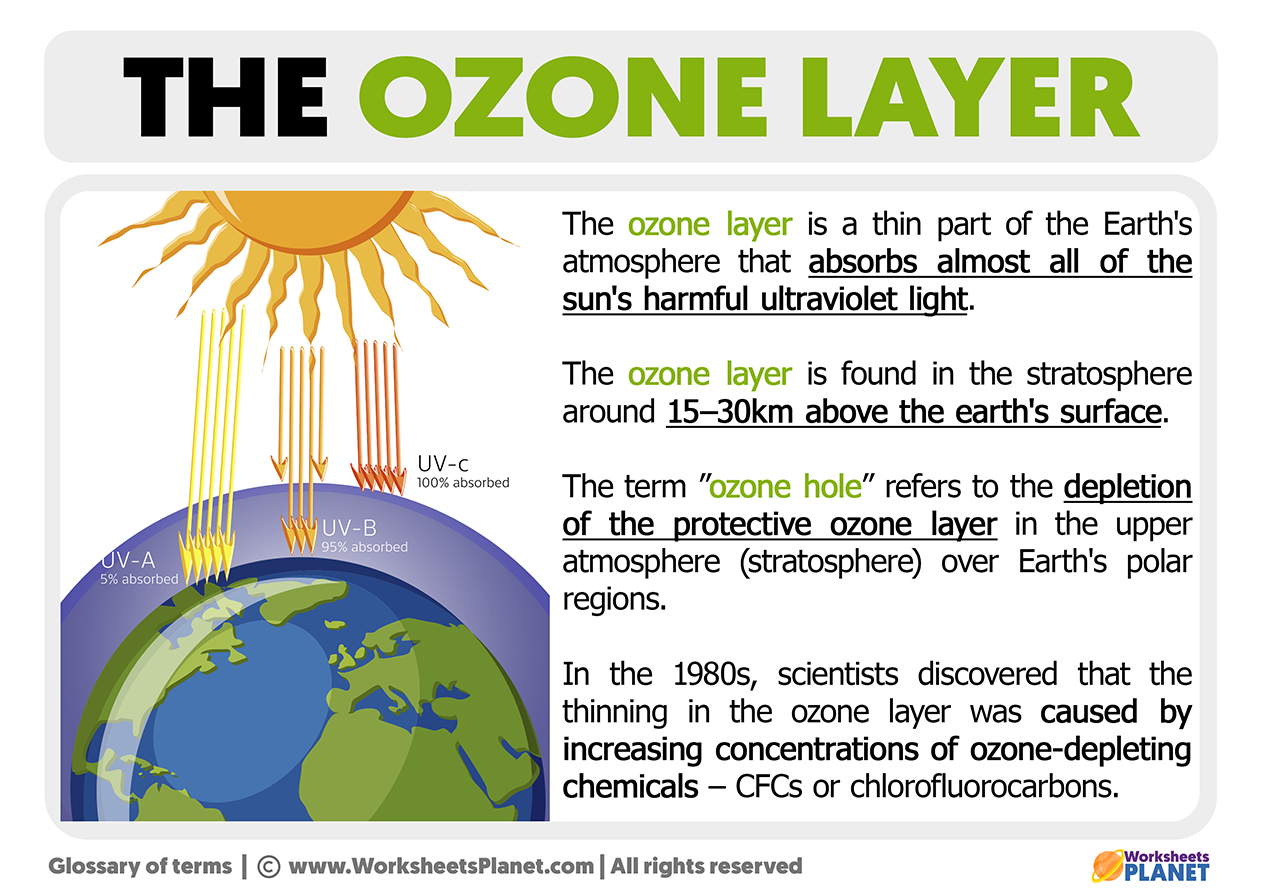
The term “ozone hole” refers to the depletion of the protecting ozone layer in the upper layer of our atmosphere (called stratosphere) over Earth’s polar areas.
In the 1980s, scientists discovered that the thinning in the ozone layer was caused by increasing concentrations of ozone-depleting chemicals – CFCs or chlorofluorocarbons.

