Symmetrical distribution refers to a pattern where the data values are distributed evenly around a central point, resulting in a balanced shape. This means that the data is equally likely to occur on either side of the center, creating a mirror image-like effect.
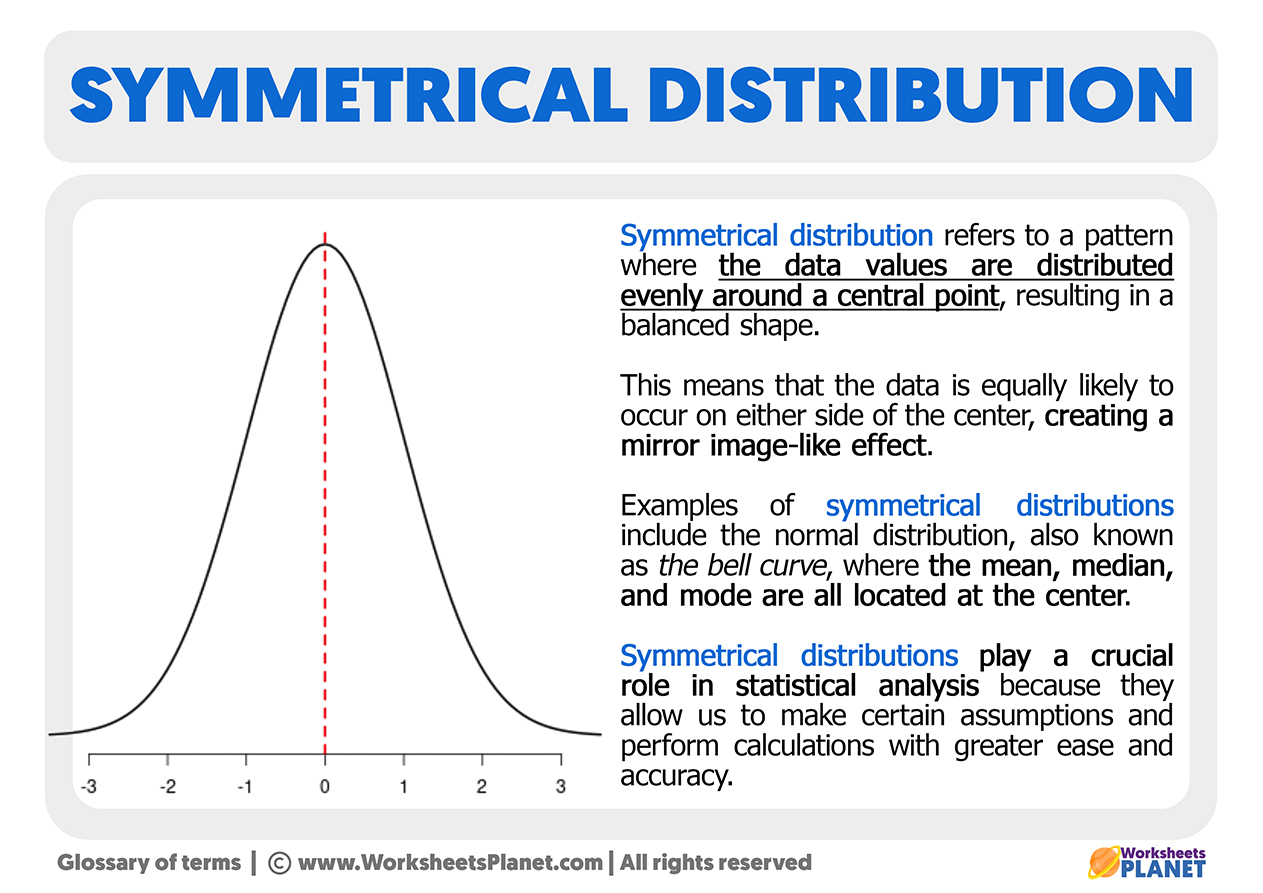
Examples of symmetrical distributions include the normal distribution, also known as the bell curve, where the mean, median, and mode are all located at the center. Symmetrical distributions play a crucial role in statistical analysis because they allow us to make certain assumptions and perform calculations with greater ease and accuracy.

