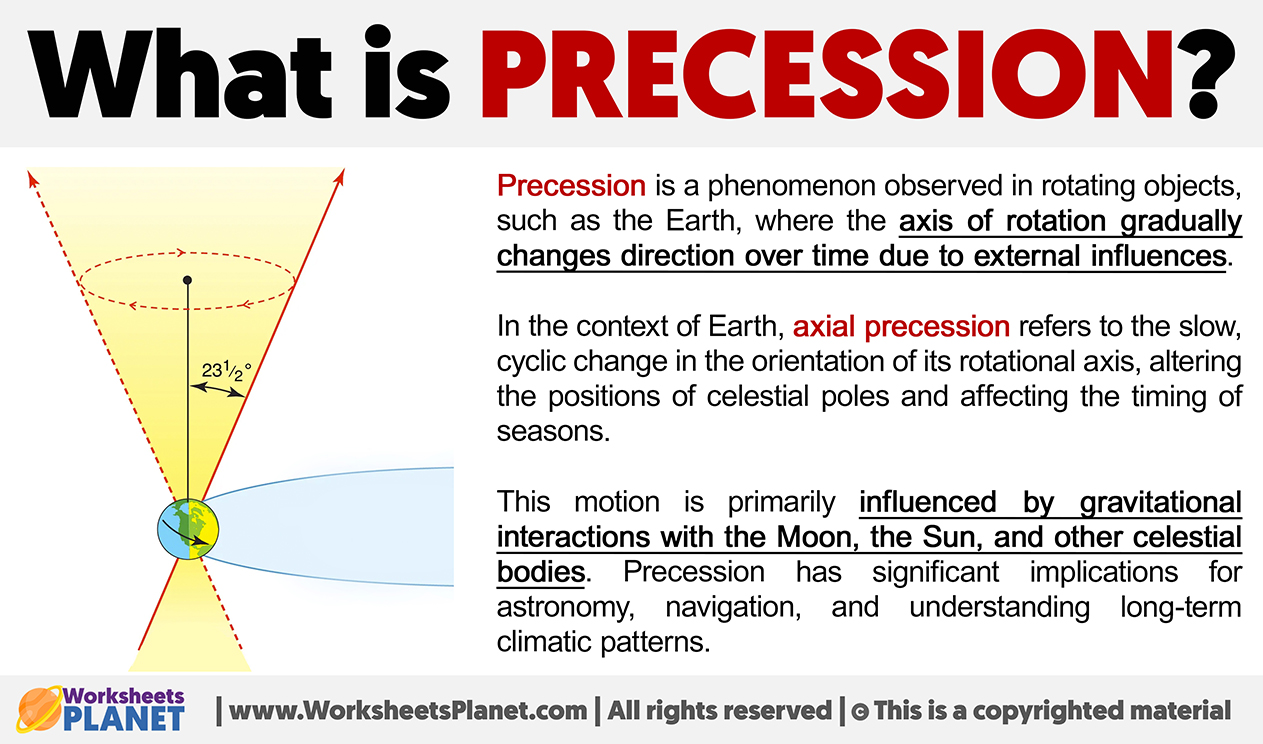
Precession is a phenomenon observed in rotating objects, such as the Earth, where the axis of rotation gradually changes direction over time due to external influences.
In the context of Earth, axial precession refers to the slow, cyclic change in the orientation of its rotational axis, altering the positions of celestial poles and affecting the timing of seasons.
This motion is primarily influenced by gravitational interactions with the Moon, the Sun, and other celestial bodies. Precession has significant implications for astronomy, navigation, and understanding long-term climatic patterns.