The large intestine, also called “the colon”, is a long tube-like organ in the digestive system responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from the remaining indigestible food matter, forming solid waste known as feces.
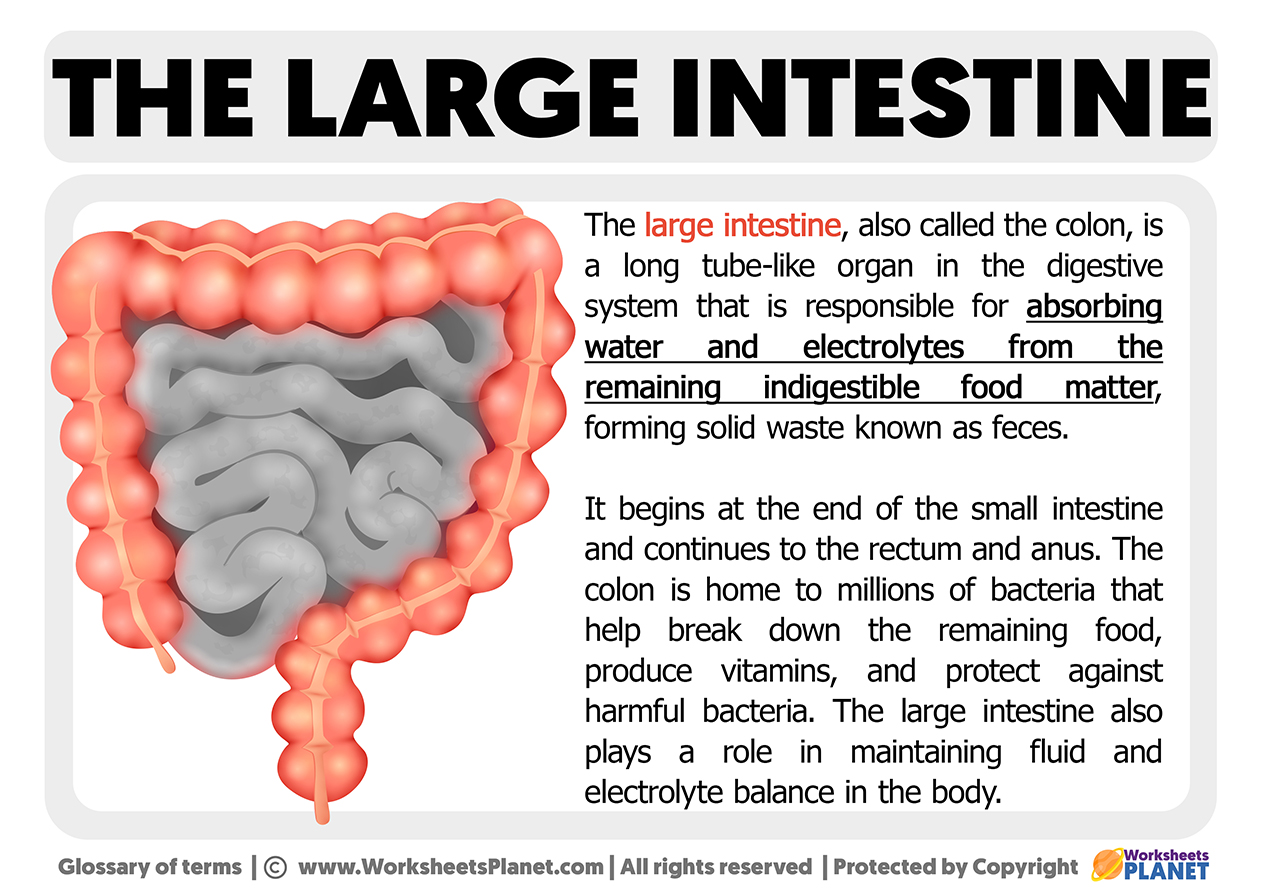
The large intestine begins at the end of the other one, the small intestine, and continues to the rectum and anus.
The colon is home to millions of bacteria that help break down the remaining food, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful bacteria.
The large intestine also plays a role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.

