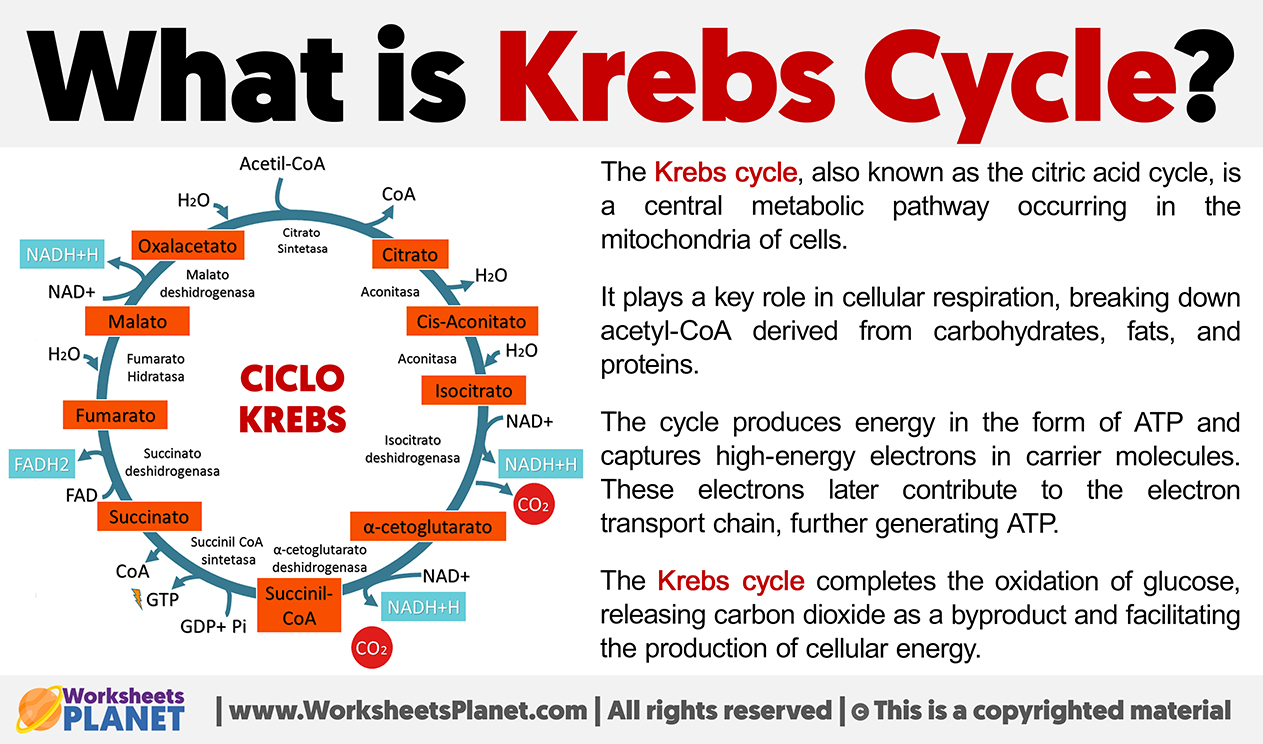
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is a central metabolic pathway occurring in the mitochondria of cells. It plays a key role in cellular respiration, breaking down acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
The cycle produces energy in the form of ATP and captures high-energy electrons in carrier molecules. These electrons later contribute to the electron transport chain, further generating ATP.
The Krebs cycle completes the oxidation reaction of glucose, releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct and facilitating the production of cellular energy.