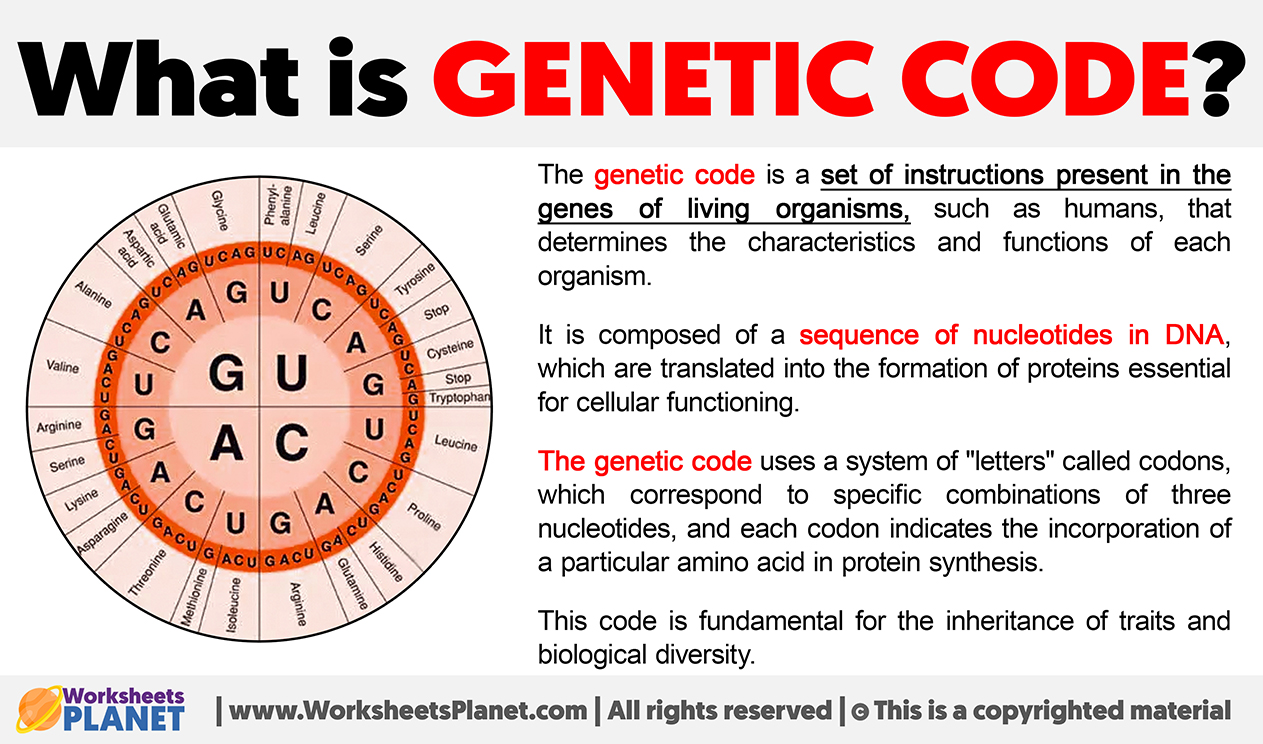
The genetic code is a set of instructions present in the genes of living organisms, such as humans, that determines the characteristics and functions of each organism.
It is composed of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA, which are translated into the formation of proteins essential for cellular functioning.
The genetic code uses a system of “letters” called codons, which correspond to specific combinations of three nucleotides, and each codon indicates the incorporation of a particular amino acid in protein synthesis. This code is fundamental for the inheritance of traits and biological diversity.