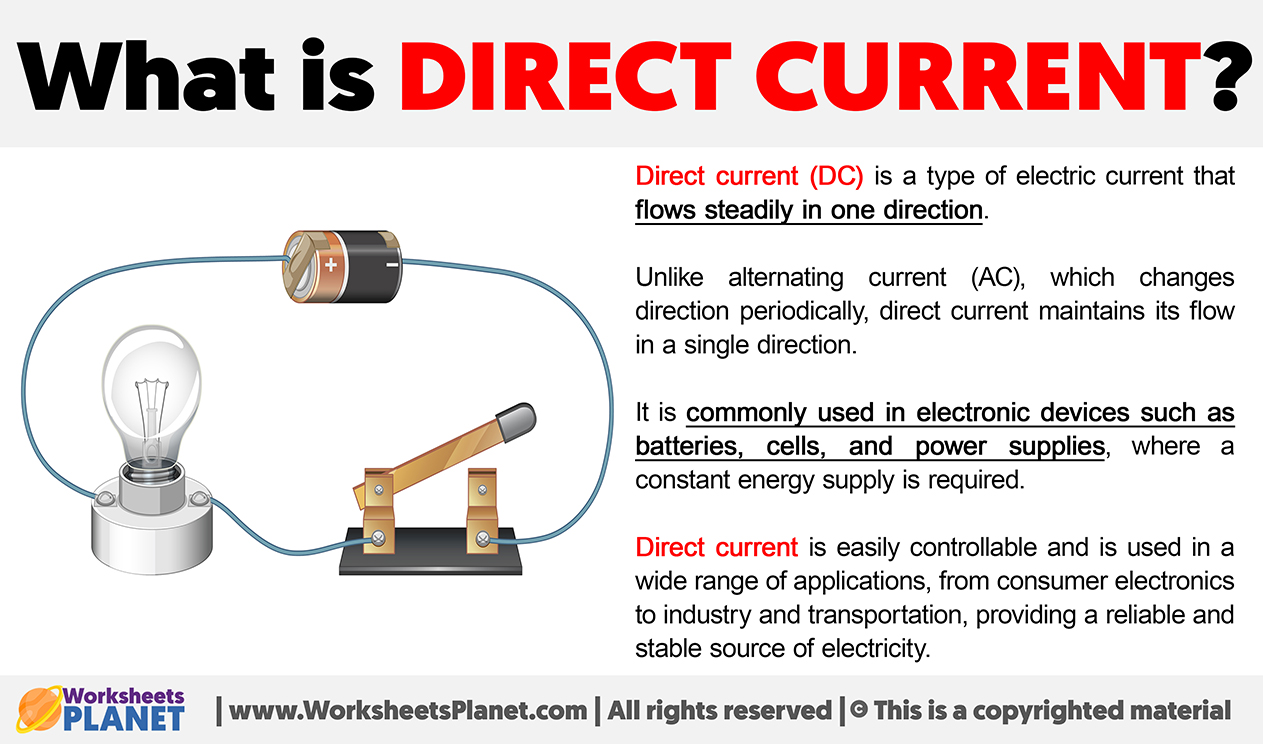
Direct current (DC) is a type of electric current that flows steadily in one direction. Unlike alternating current (AC), which changes direction periodically, direct current maintains its flow in a single direction.
It is commonly used in electronic devices such as batteries, cells, and power supplies, where a constant energy supply is required.
Direct current is easily controllable and is used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industry and transportation, providing a reliable and stable source of electricity.