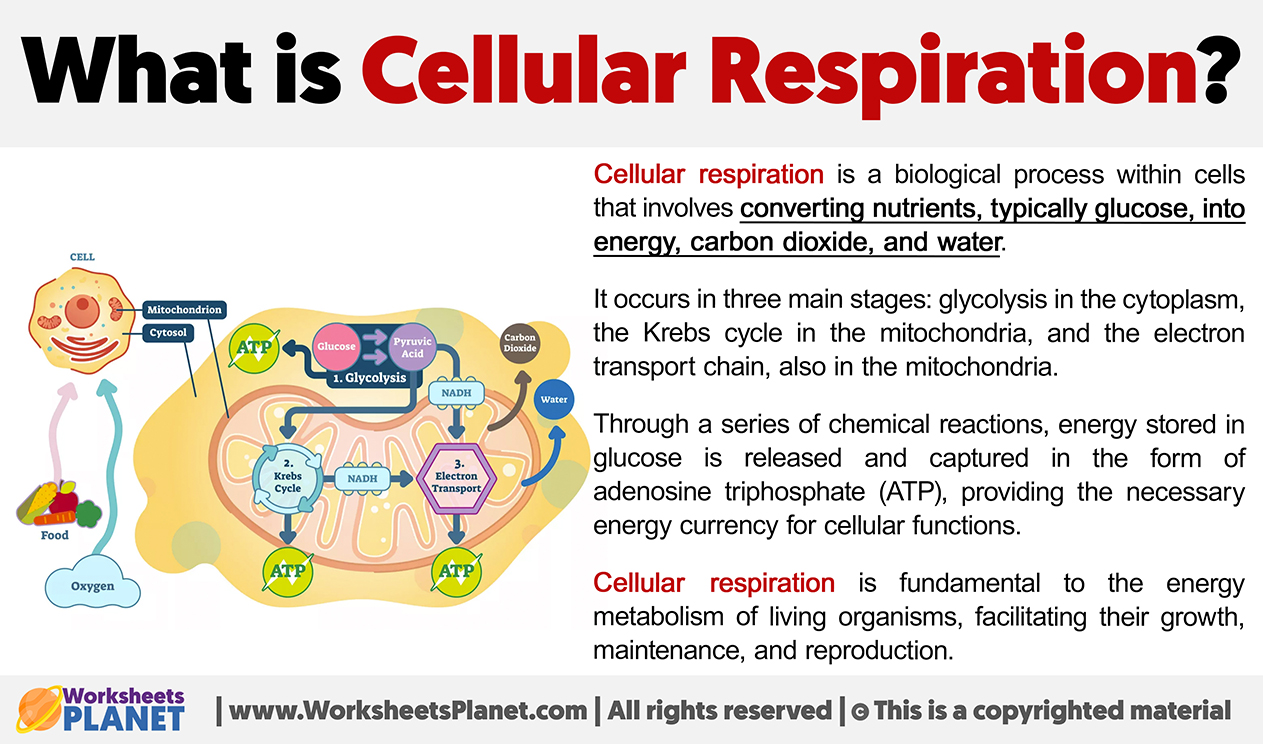
Cellular respiration is a biological process within cells that involves converting nutrients, typically glucose, into energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
It occurs in three main stages: glycolysis in the cytoplasm, the Krebs cycle in the mitochondria, and the electron transport chain, also in the mitochondria.
Through a series of chemical reactions, energy stored in glucose is released and captured in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), providing the necessary energy currency for cellular functions.
Cellular respiration is fundamental to the energy metabolism of living organisms, facilitating their growth, maintenance, and reproduction.