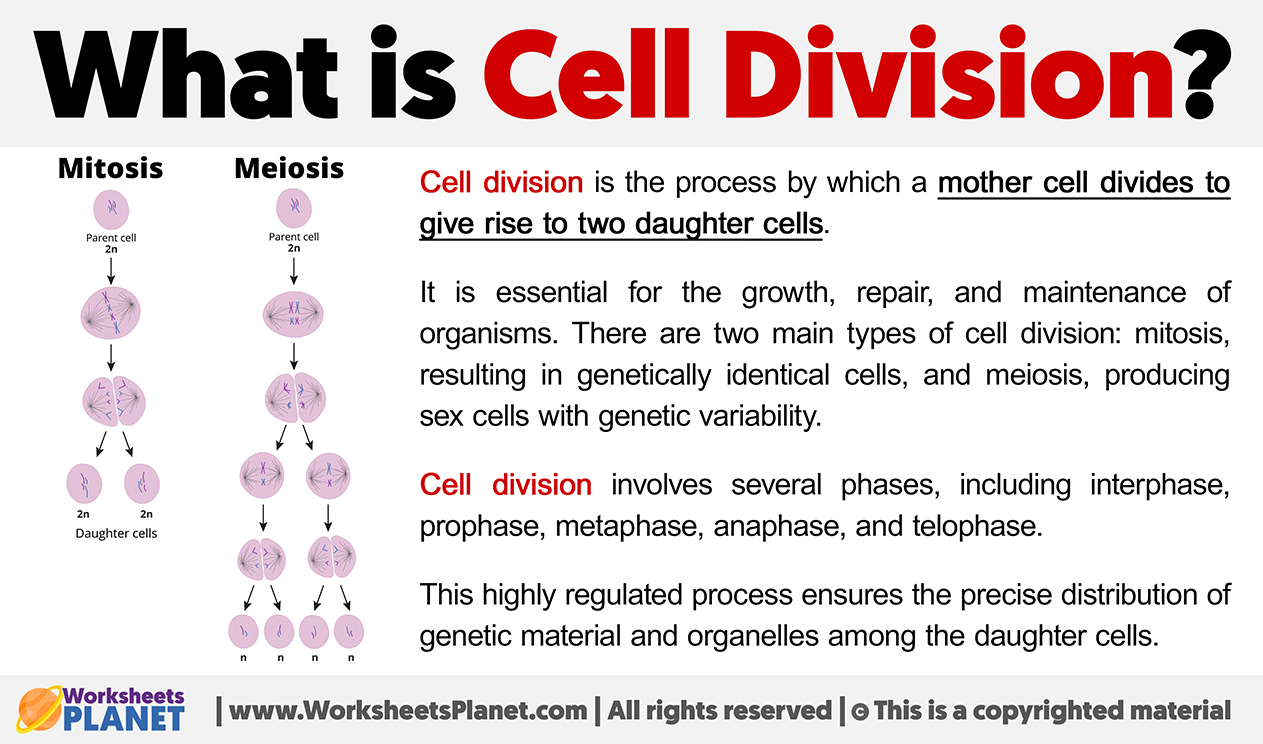
Cell division is the process by which a mother cell divides to give rise to two daughter cells. It is essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of organisms.
There are two main types of cell division:
- Mitosis, resulting in genetically identical cells.
- Meiosis, producing sex cells with genetic variability.
Cell division involves several phases, including interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. This highly regulated process ensures the precise distribution of genetic material and organelles among the daughter cells.