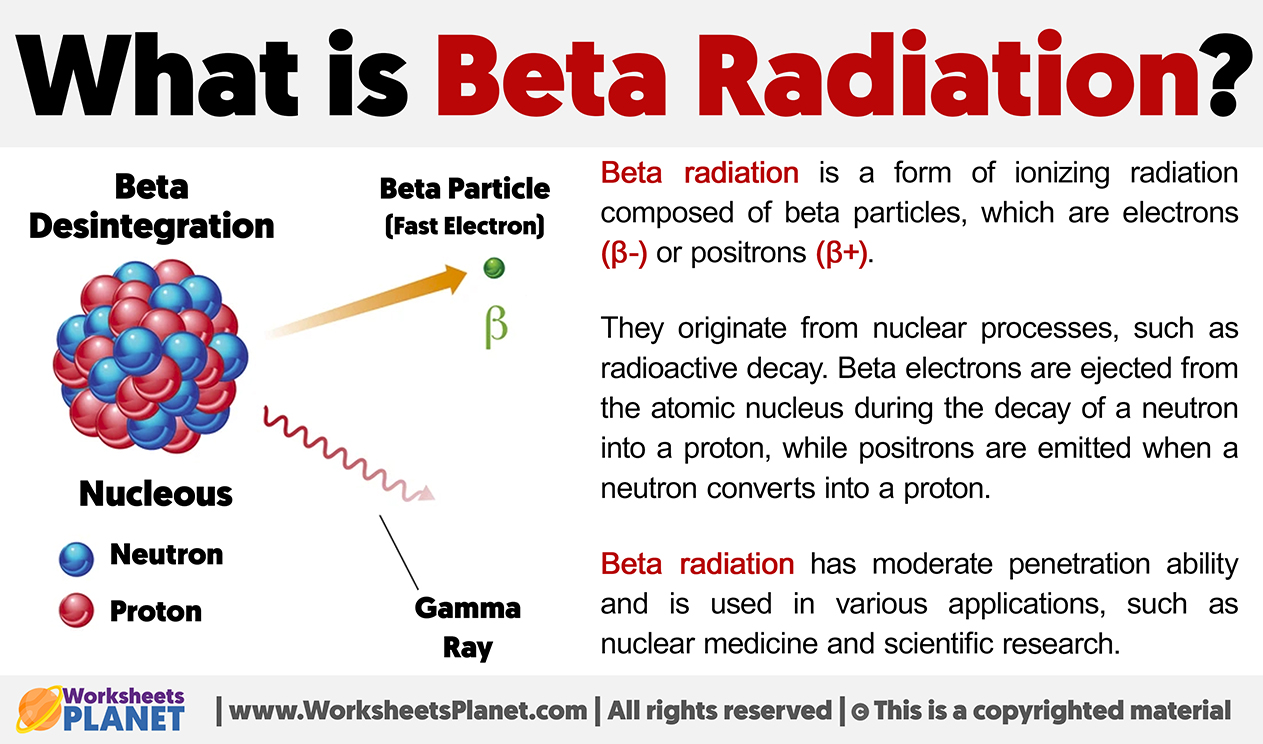
Beta radiation is a form of ionizing radiation composed of beta particles, which are electrons (β-) or positrons (β+).
They originate from nuclear processes, such as radioactive decay. Beta electrons are ejected from the atomic nucleus during the decay of a neutron into a proton, while positrons are emitted when a neutron converts into a proton.
Beta radiation has moderate penetration ability and is used in various applications, such as nuclear medicine and scientific research.