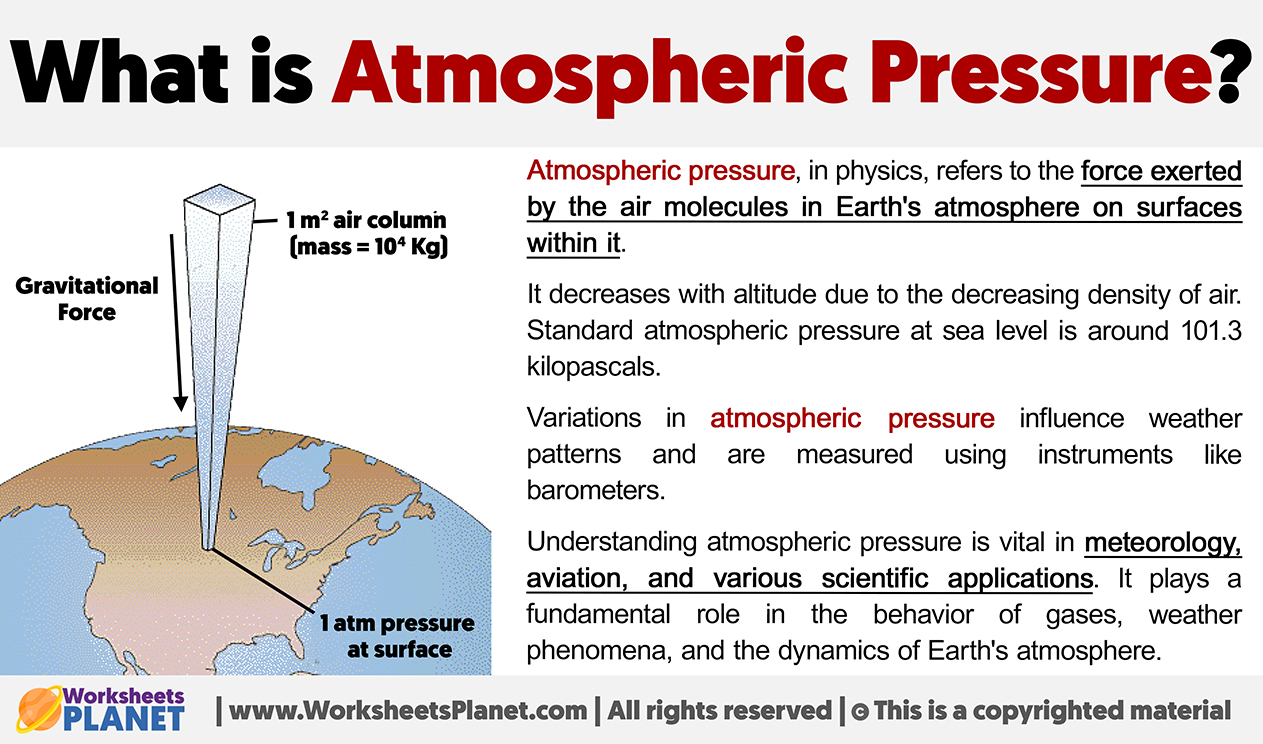
Atmospheric pressure, in physics, refers to the force exerted by the air molecules in Earth’s atmosphere on surfaces within it.
It decreases with altitude due to the decreasing density of air. Standard atmospheric pressure at sea level is around 101.3 kilopascals. Variations in atmospheric pressure influence weather patterns and are measured using instruments like barometers.
Understanding atmospheric pressure is vital in meteorology, aviation, and various scientific applications. It plays a fundamental role in the behavior of gases, weather phenomena, and the dynamics of Earth’s atmosphere.