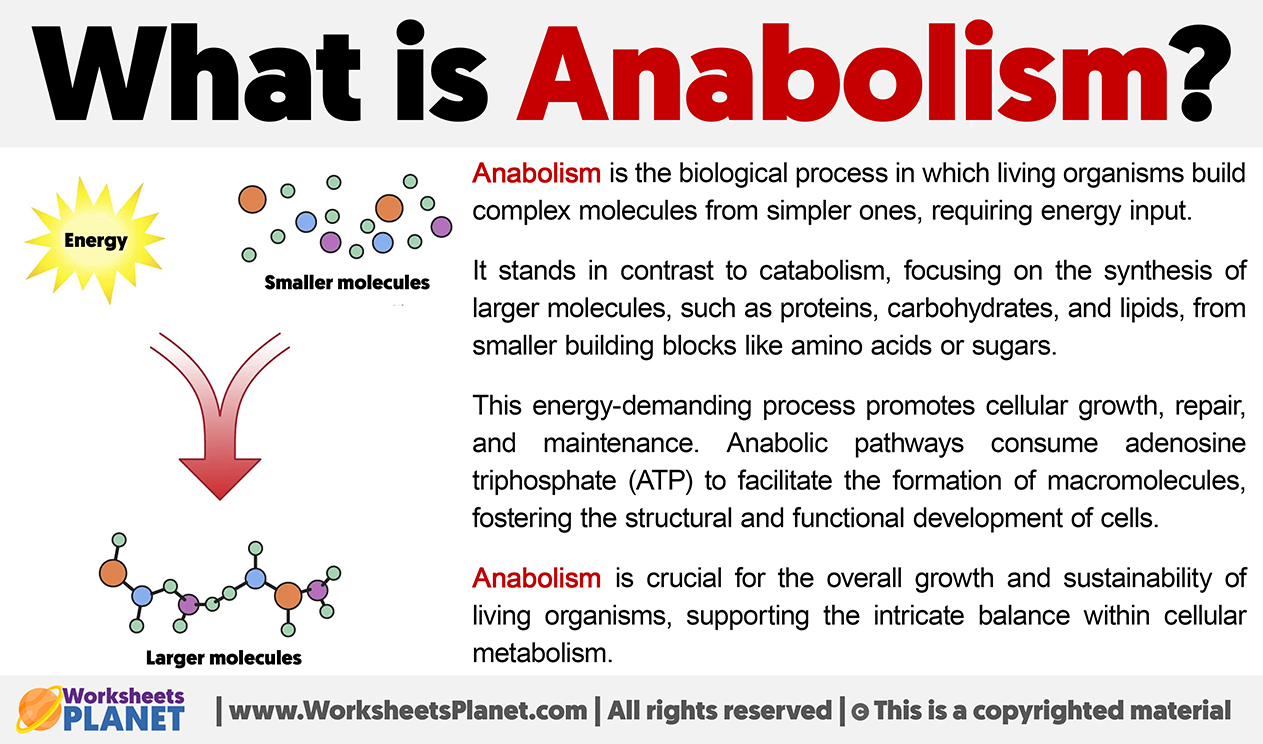
Anabolism is the biological process in which living organisms build complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input.
It stands in contrast to catabolism, focusing on the synthesis of larger molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from smaller building blocks like amino acids or sugars.
This energy-demanding process promotes cellular growth, repair, and maintenance. Anabolic pathways consume adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to facilitate the formation of macromolecules, fostering the structural and functional development of cells.
Anabolism is crucial for the overall growth and sustainability of living organisms, supporting the intricate balance within cellular metabolism.

