An ecosystem is a physical and biological system formed by a community of living beings that inhabit a delimited physical environment. It is a set of physical and biological factors particular to a specific environment. In an ecosystem, exists a relationship of interdependence between the different elements that make it up. A change in one link in the chain can have consequences in a completely different and distant connection. This alteration can lead to a break in the planet’s ecological balance.
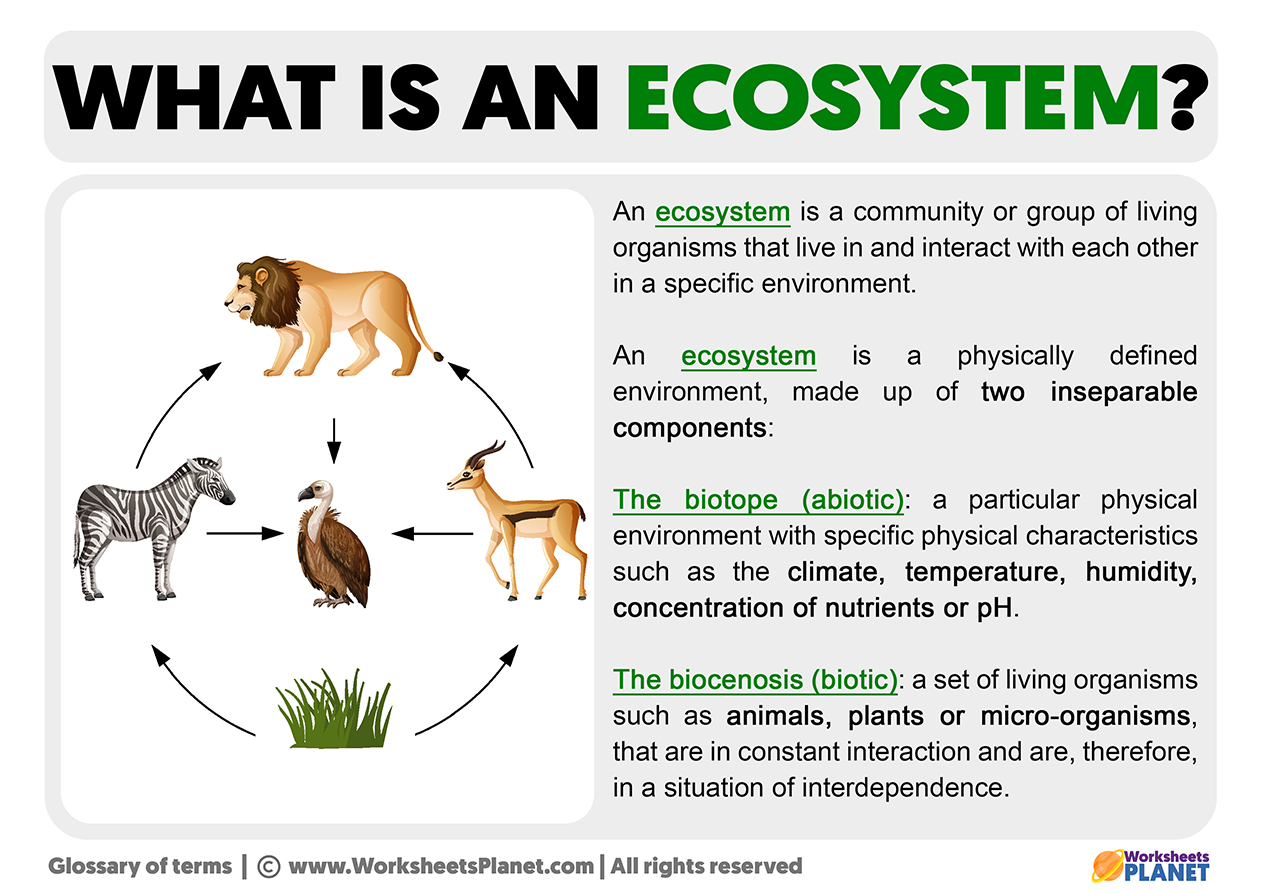
The concept of ecosystems considers the complex interactions between the organisms that make up the community (biocenosis) and the flows of energy and materials that cross it. This term implies the relationships between different living beings and how they interact with their environment.
An example of this type of interaction is the trophic or food chain, the process of transferring food from one organism to another. The food chain shows us the feeding relationships between living beings and establishes which animal eats whom.
The food chain is made up of three groups: producers, which refers to plants capable of generating their own food; the primary consumers, which are the carnivorous animals whose food depends on others; and, finally, the decomposers, which feed on organisms that decompose until they become part of the soil.
All living beings involved in the food chain are interdependent, which means they depend on each other to form a certain balance. The alteration or rupture of some of these levels can cause ecological damage as serious as the disappearance of certain species.

