Acid rain is a tremendously harmful phenomenon for our planet that is formed when the humidity of the Earth’s atmosphere comes into contact with harmful chemical elements, usually emitted by factories, power plants, and vehicles.
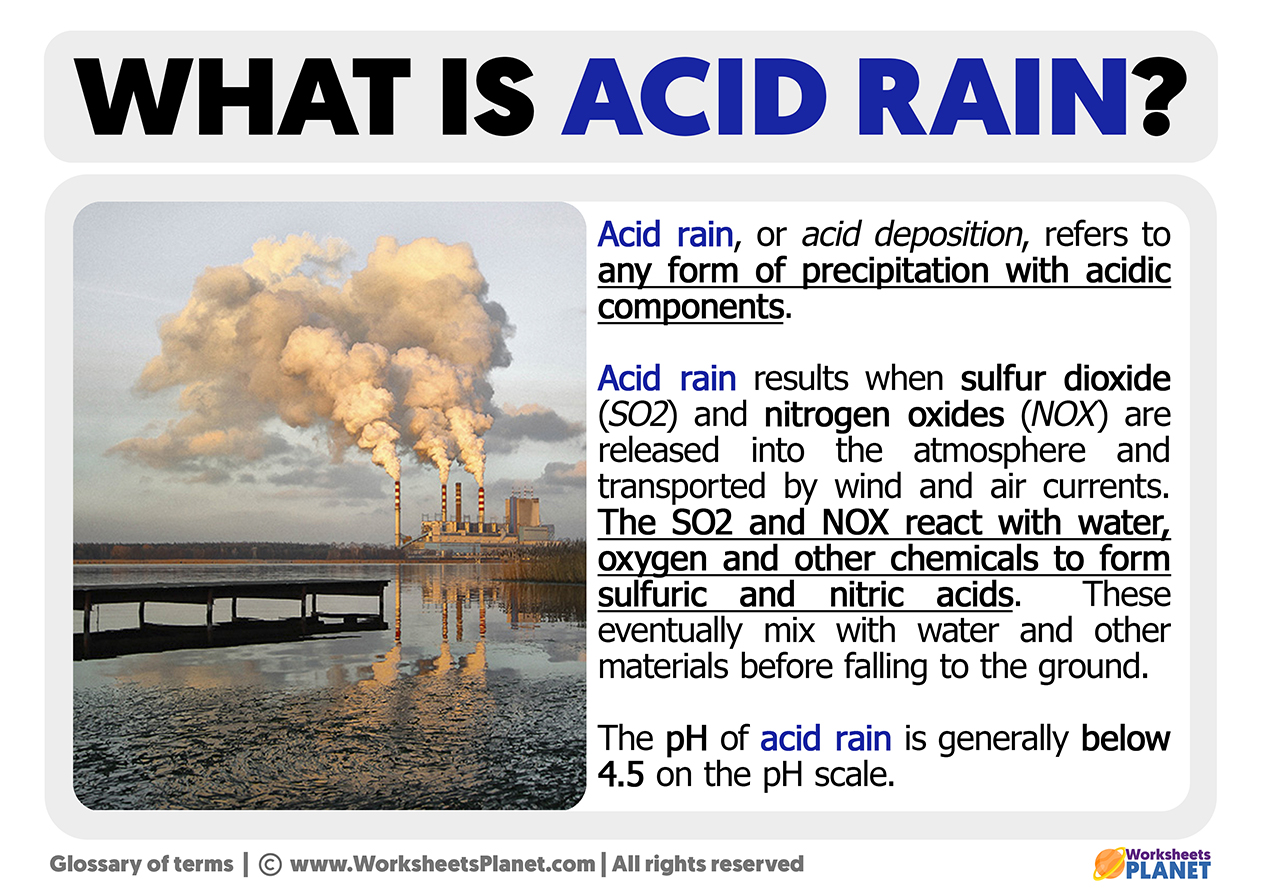
Acid rain, or acid deposition, refers to any condition of precipitation with acidic elements. Acid precipitation is a consequence that occurs when sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOX) are emitted into the atmosphere and transported by wind and air currents.
These two chemical elements, SO2 and NOX, react with water, oxygen, and additional chemicals to form sulfuric and nitric acids. These eventually mix with water and other materials before falling to the ground. The pH of acid rain is generally below 4.5 on the pH scale.

