The term proton comes from the Greek prōton, which means first. It is a subatomic particle found within the nucleus of atoms and has a positive electrical charge. The protons have the same absolute value than the electrons but their representation is the opposite. So the proton has a positive electric charge, and the electron has a negative charge.
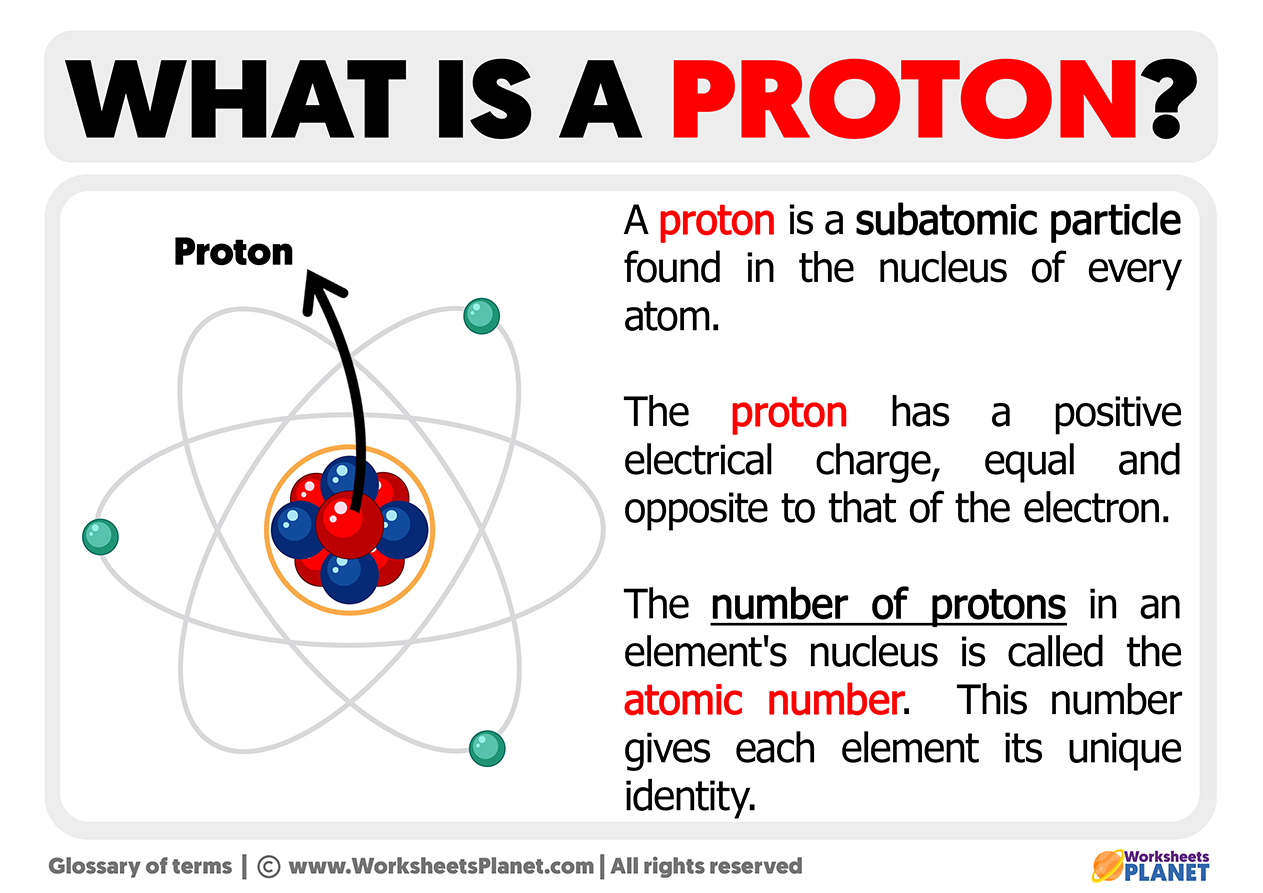
You could say protons are about the same size as electrons; protons combine with protons and neutrons to form atoms.
How are protons formed?
Protons are subatomic particles composed of three quarks held together by strong nuclear interaction; these three quarks have ½ spin and are arranged: two up quarks and one down quark.
What is the electrical charge of these quarks?
- Up quarks have an electrical charge of +2/3.
- Down quarks have an electrical charge of -1/3.
Characteristics of Protons
- Mass: The proton’s mass is about 1836 times greater than the electron’s; it has a mass of about 1.674 x 1024g, about the same as neutrons.
- Electrical charge: Protons have the same absolute charge than electrons, just positively charged. Its charge is equal to 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs.
- Life of the proton: Protons are stable particles that do not disintegrate into other particles. Its life is considered eternal on an experimental level; it is given a half-life of about 1035 years and a life of more than 2.1 x 1029 years.
- Measure: The proton is about 0.88 femtometers wide, that is, 10−15 meters.
- Protons are nucleons: Protons and neutrons are found in the atom’s nucleus, which is why they are called nucleons.
- Protons have an antiparticle: Protons have an antiparticle called “antiproton,” characterized by a negative charge.
- They are composite particles: Protons are particles made up of smaller structures called hadrons, which are made up of quarks (they contain the electrical charge of the proton).

