In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially adopted a definition for planet and the other bodies in the Solar System. At this moment, as a consequence of the stablished definition, scientists decided Pluto was no longer considered a planet, it turned into a dwarf planet.
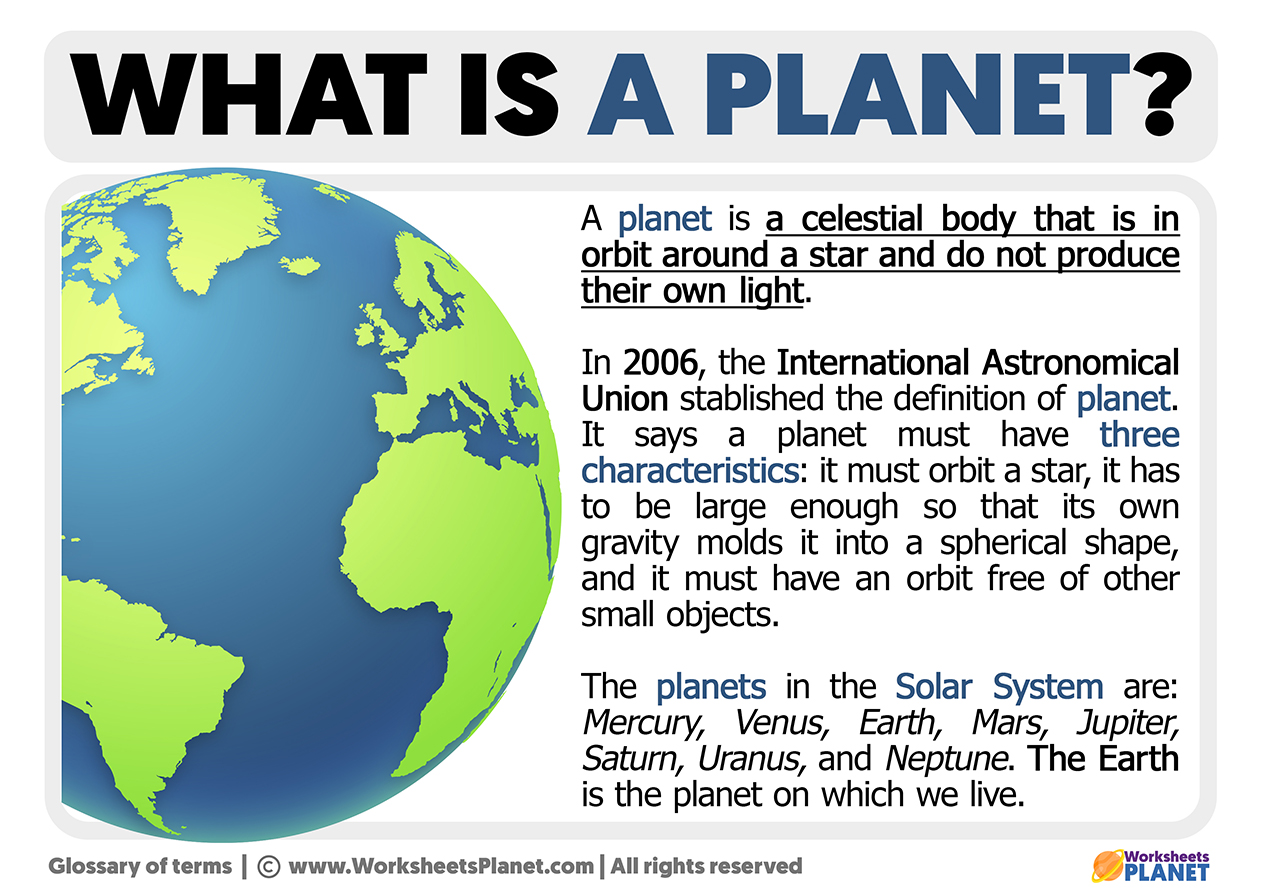
For a celestial object in the Solar System to be considered a planet, it must meet the following requirements:
- It has to orbit around the Sun.
- Its mass must be heavy enough that the object’s gravity dominates the forces as a rigid body.
- It has a rounded or spherical shape.
- It is the dominant object in its “neighborhood”, which has cleaned its orbit.
On the other hand, it is considered a dwarf planet:
- Those objects that orbit around the sun.
- It has enough mass for its gravity to dominate the forces present in hydrostatic equilibrium and with a rounded shape.
- Dwarf planets have not cleared other objects from their orbit.
- It is not a satellite of another planet.
- The rest of the objects of the Solar System that are not satellites will be called small bodies of the Solar System.

