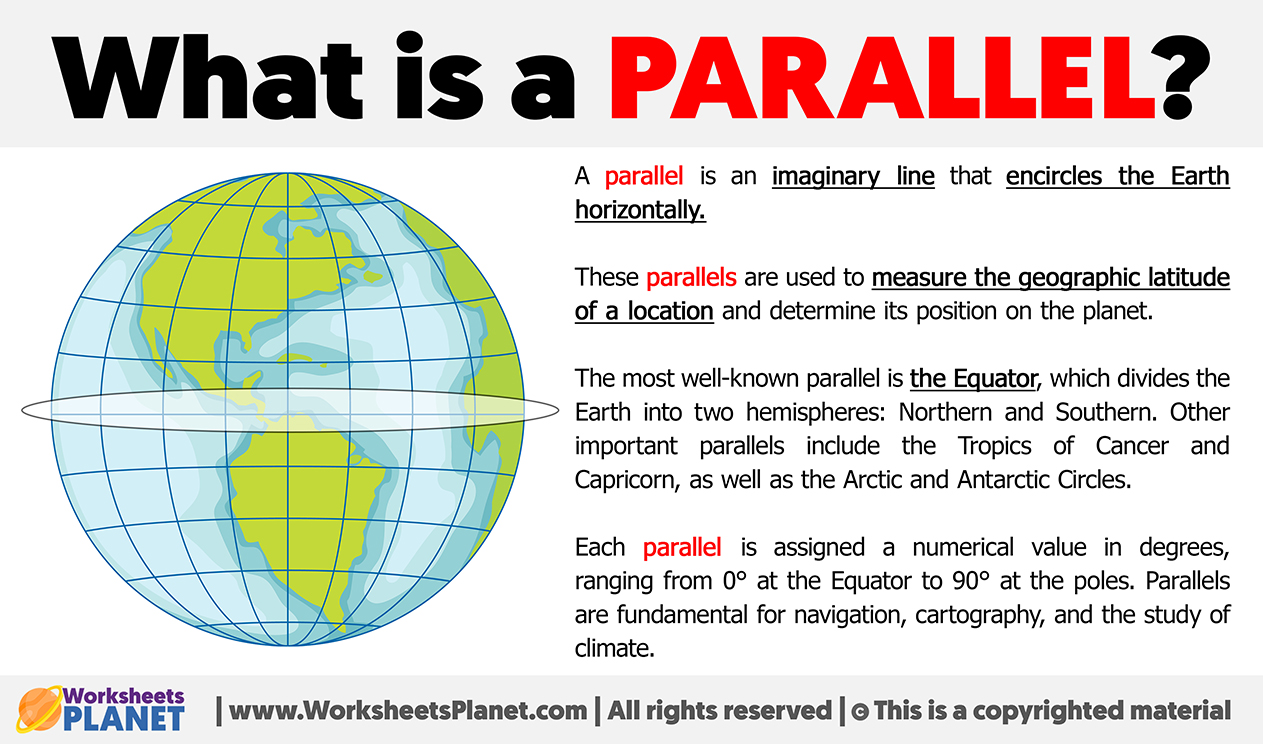
A parallel is an imaginary line that encircles the Earth horizontally. These parallels are used to measure the geographic latitude of a location and determine its position on the planet.
The most well-known parallel is the Equator, which divides the Earth into two hemispheres: Northern and Southern. Other important parallels include the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, as well as the Arctic and Antarctic Circles.
Each parallel is assigned a numerical value in degrees, ranging from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles. Parallels are fundamental for navigation, cartography, and the study of climate.