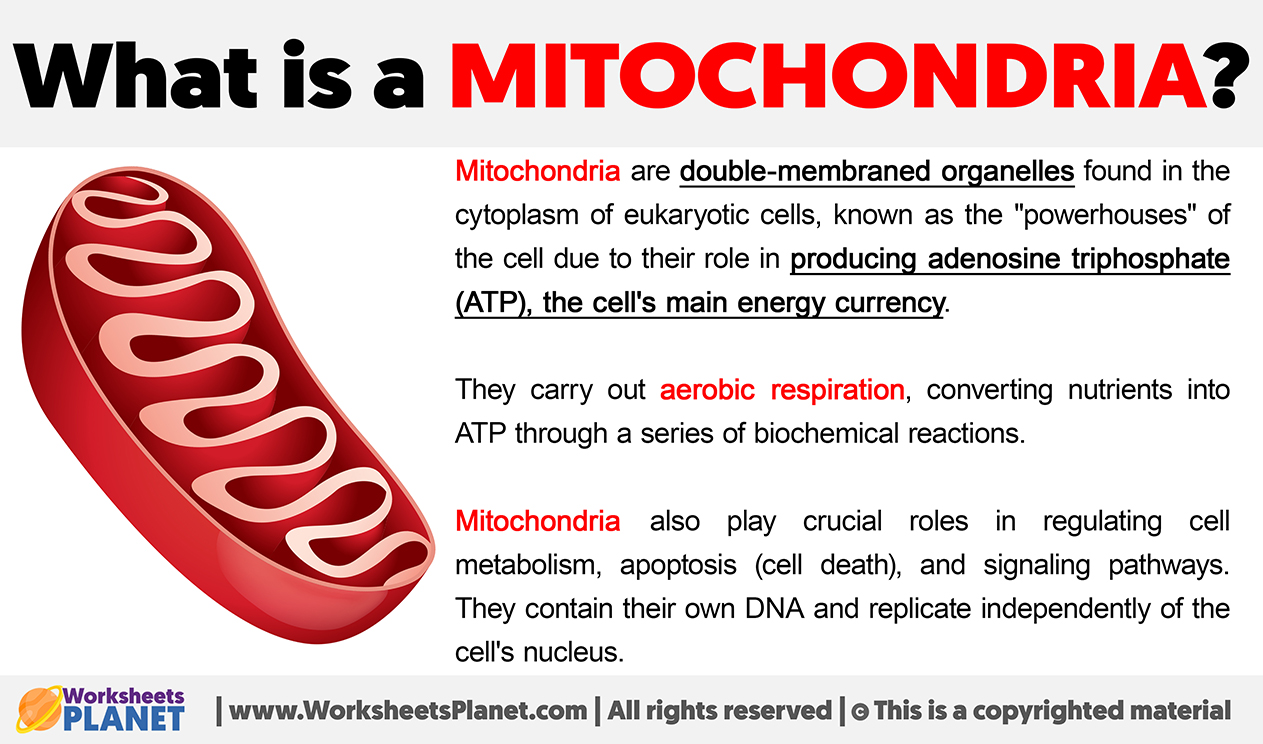
Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, known as the “powerhouses” of the cell due to their role in producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy currency.
They carry out aerobic respiration, converting nutrients into ATP through a series of biochemical reactions.
Mitochondria also play crucial roles in regulating cell metabolism, apoptosis (cell death), and signaling pathways. They contain their own DNA and replicate independently of the cell’s nucleus.