A balance is a measuring device designed to determine the mass of an object by comparing it to a known mass.
It typically consists of a horizontal beam, a fulcrum, and pans on either side. By placing the object on one pan and adding calibrated weights to the other, equilibrium is achieved when the beam is level.
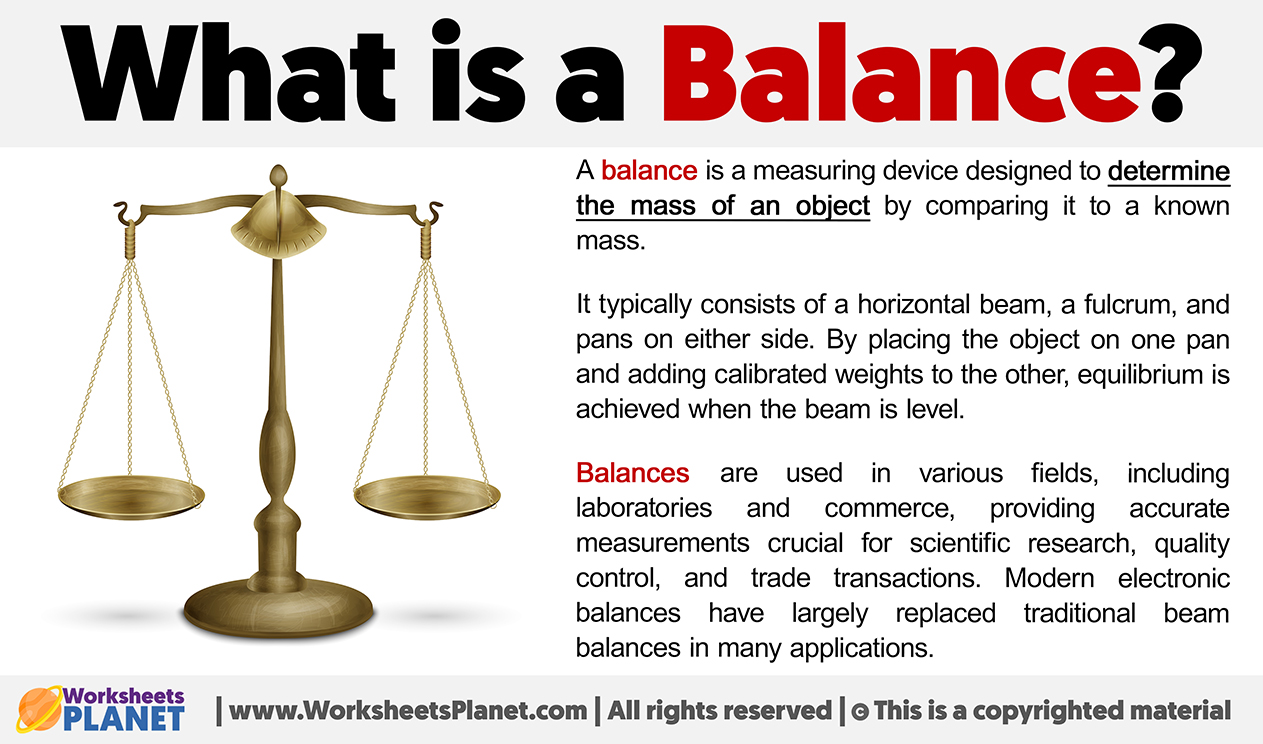
Balances are used in various fields, including laboratories and commerce, providing accurate measurements crucial for scientific research, quality control, and trade transactions. Modern electronic balances have largely replaced traditional beam balances in many applications.

