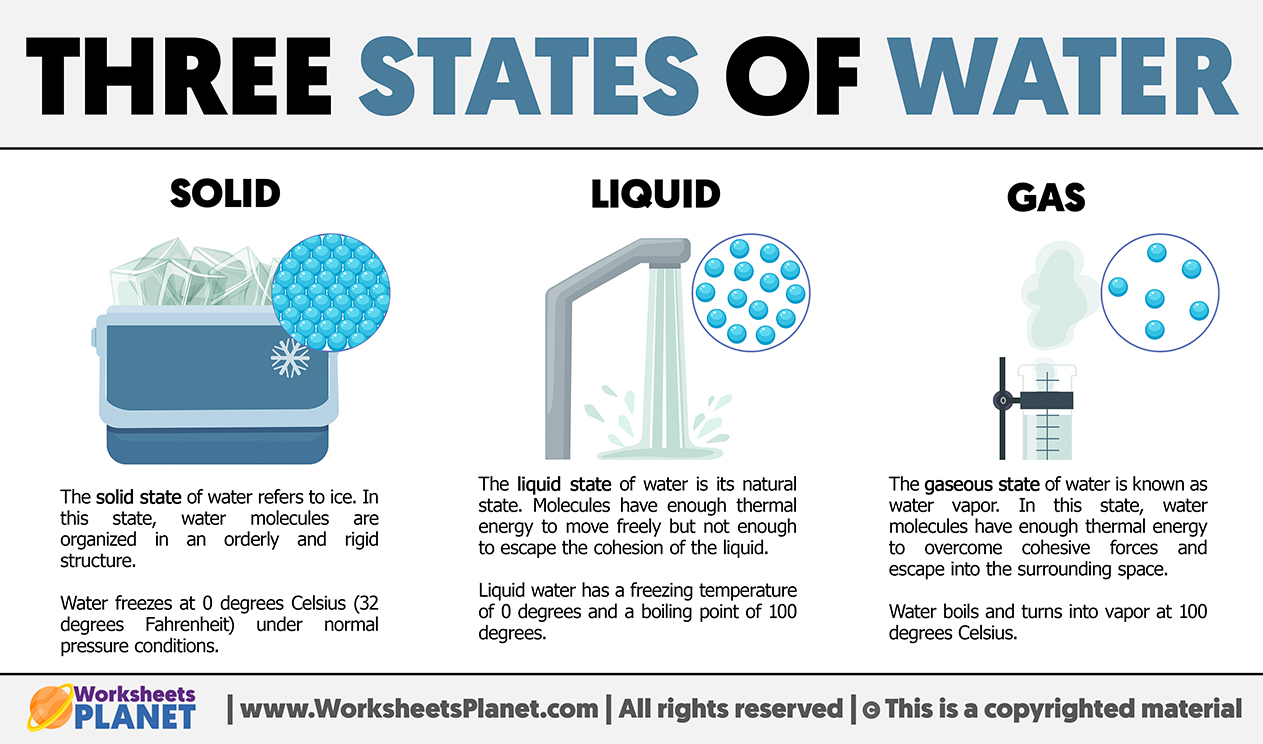
Water exists in three main states: solid, liquid, and gas. Each state represents a distinct phase characterized by unique properties and behaviors of water molecules.
- Solid: the solid state of water refers to ice. In this state, water molecules are organized in an orderly and rigid structure. Water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit) under normal pressure conditions.
- Liquid: the liquid state of water is its natural state. Molecules have enough thermal energy to move freely but not enough to escape the cohesion of the liquid. Liquid water has a freezing temperature of 0 degrees and a boiling point of 100 degrees.
- Gas: the gaseous state of water is known as water vapor. In this state, water molecules have enough thermal energy to overcome cohesive forces and escape into the surrounding space. Water boils and turns into vapor at 100 degrees Celsius.