Neurons are the most important cells of the nervous system. Since they control both voluntary and involuntary functions of the body. We have approximately 86 billion neurons in our human brain. Still, there are indeed studies that confirm every day, we lose thousands of them. For example, people between the ages of 20 and 30 lose approximately 10,000 neurons daily. That is why it is so important to keep our brains active.
Neuron Function
The primary and main functions of all types of neurons are:
- First, receive information and signals from the environment.
- Integrate and process said signals to determine if the information should be transmitted.
- Transmit information and signals to the muscles, glands…
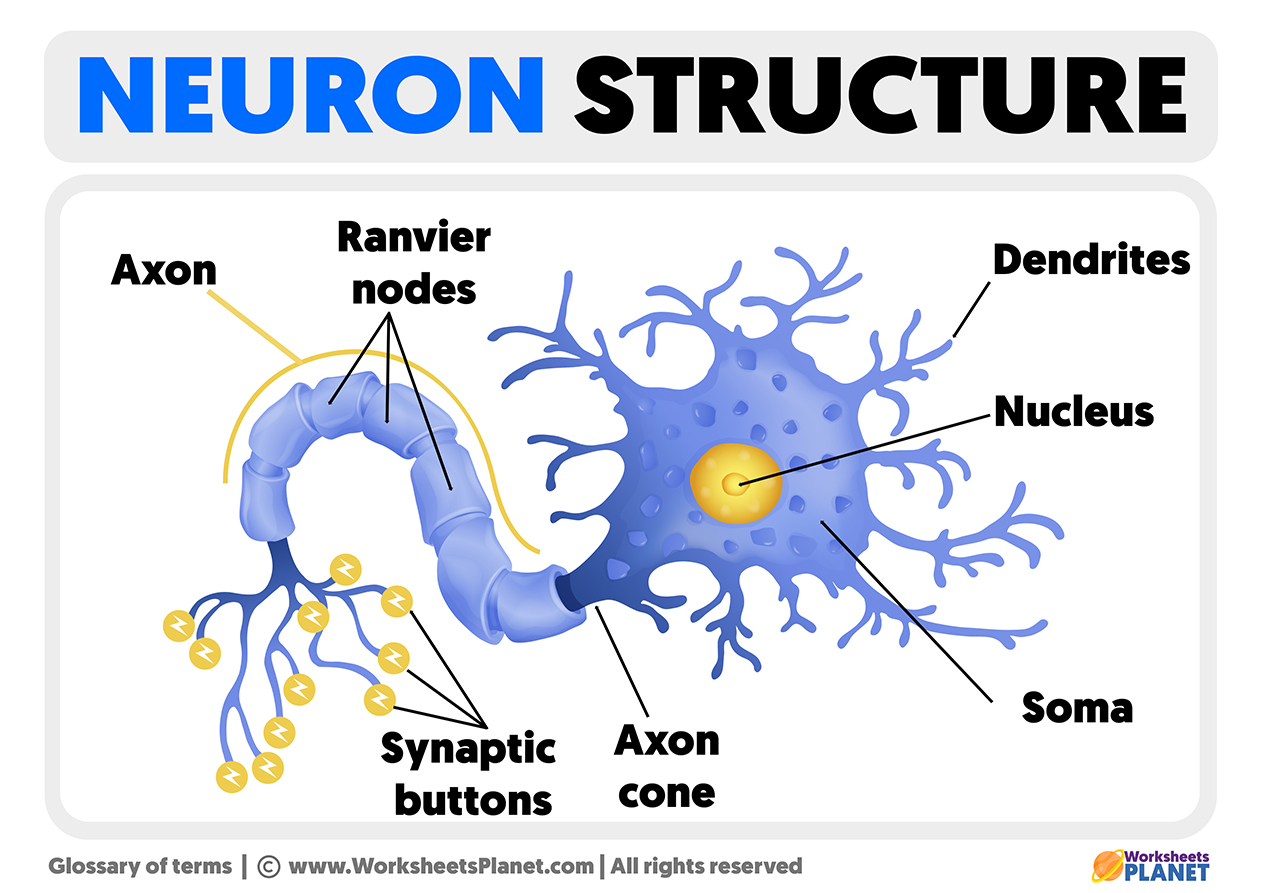
Structure of a Neuron
Neurons can be divided into up to 9 different parts, which are as follows:
Soma: This part can also be called the body of the neuron. It is where the entire genetic composition of the neuron is found and where the molecules that enable the cell’s survival are synthesized.
Nucleus: The nucleus is the most essential part of all types of cells. Apart from controlling all the genetic material, it is the central base of the neuron.
Axon: It is a fine nerve fiber wrapped in myelin sheaths. Its principal function is to transmit electrical signals from the neuron’s soma to the terminal axons.
Dendrites: this part of the neuron is responsible for capturing neurotransmitters produced by the nearest neuron and sending chemical information to the neuron body.
Myelin sheath: covers the axon of the neuron. It is a substance made up of proteins and fats that allows electrical transmission throughout the entire neuron to diffuse adequately. Some pathologies, such as Multiple Sclerosis, directly affect this part of the neuron.
Ranvier nodes: this is the gap between each myelin sheath that facilitates the conduction of the nerve impulse and prevents it from being lost.
Nissl substance: a group of granules in the cytoplasm of the neuron responsible for synthesizing proteins for neurons.
Synaptic buttons: allow neurotransmitters to be released into the external environment once the electrical impulse has been transmitted through the axon.
Axon cone: Is the part of the neuron’s body that narrows to originate the axon.

