Meiosis is a process of cell division that consists of two cellular divisions, which we call meiosis I and meiosis II, each with four different phases:
Meiosis I
Prophase I: In this phase, DNA condenses into homologous chromosomes.
Metaphase I: Here, homologous chromosomes align at the cell‘s equator.
Anaphase I: In this phase, homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase I: Finally, chromosomes unravel, and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
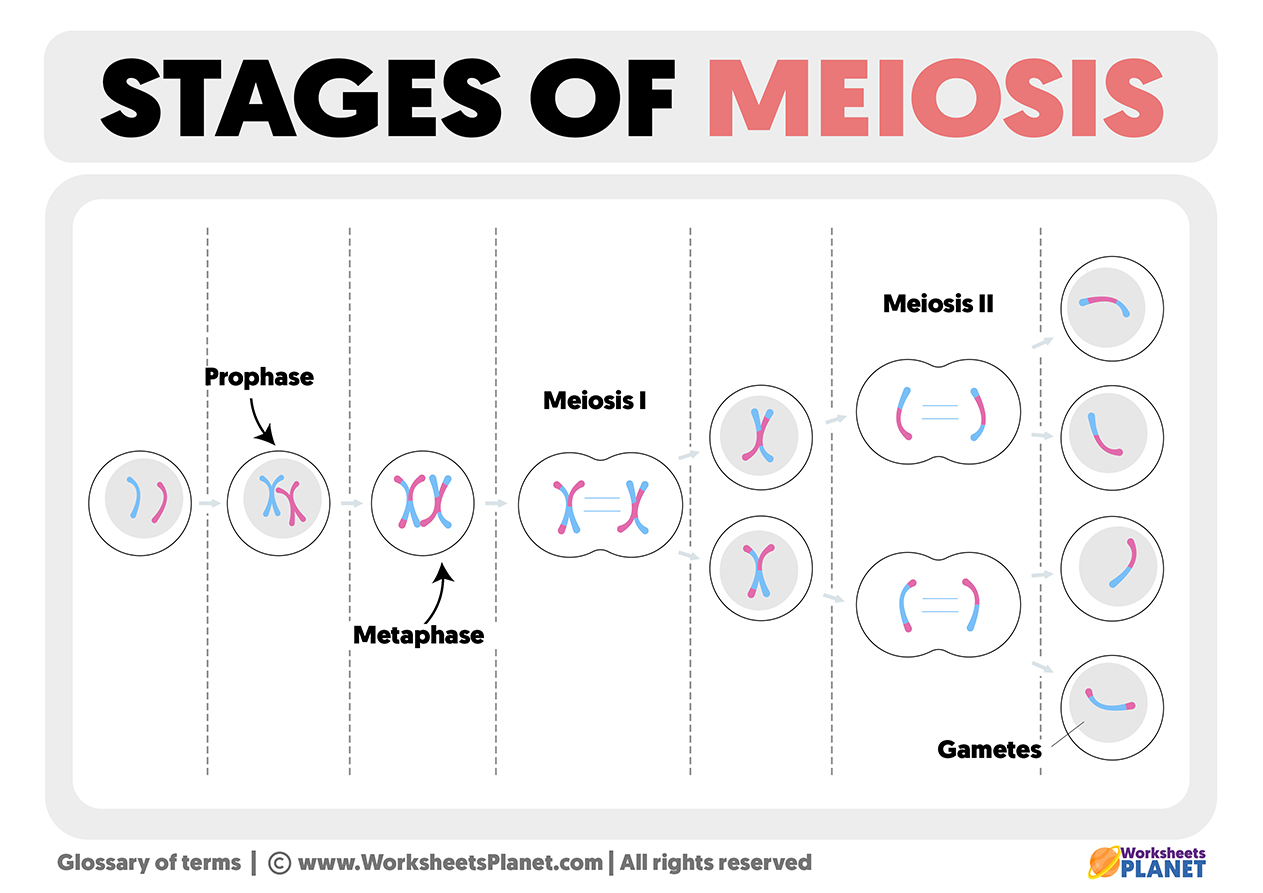
Meiosis II
Prophase II: The chromosomes condense again.
Metaphase II: Chromosomes align at the cell’s equator.
Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II: Chromosomes unravel, the cell divides, and four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes are formed.

