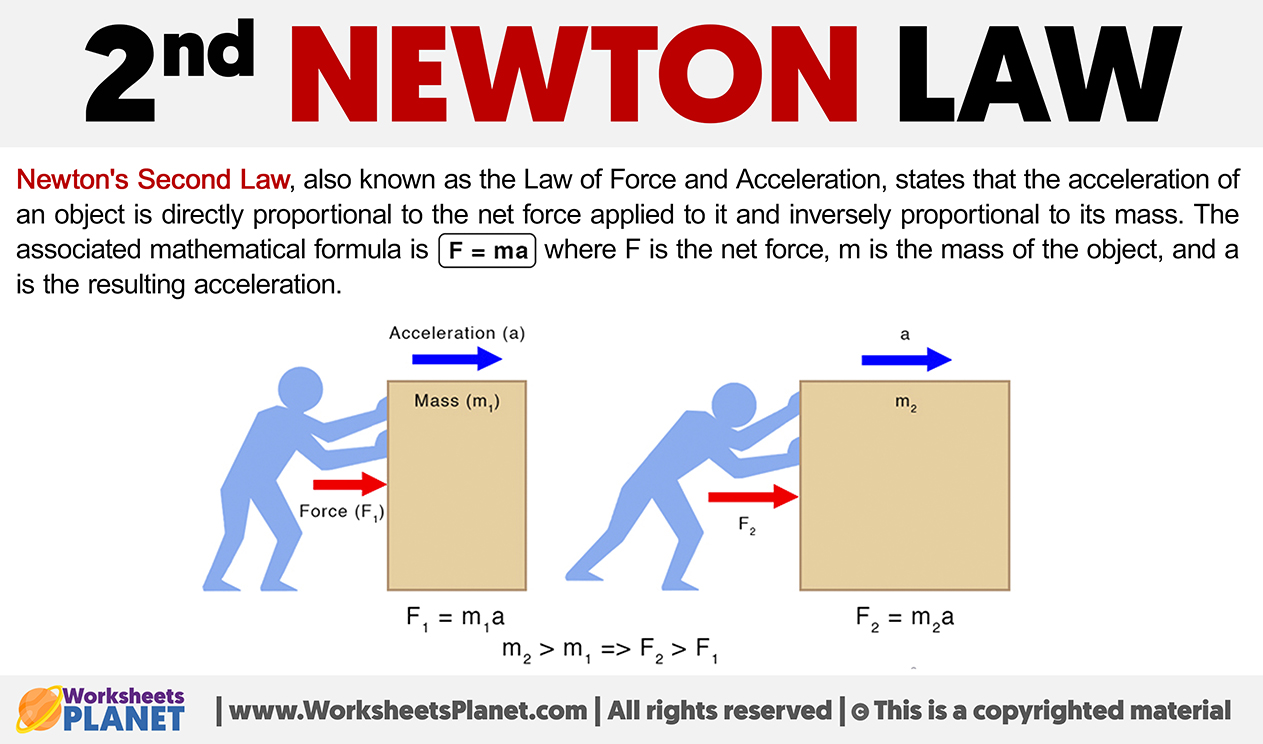
Newton’s Second Law, also known as the Law of Force and Acceleration, states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass.
The associated mathematical formula is F = m . a, where F is the net force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the resulting acceleration.