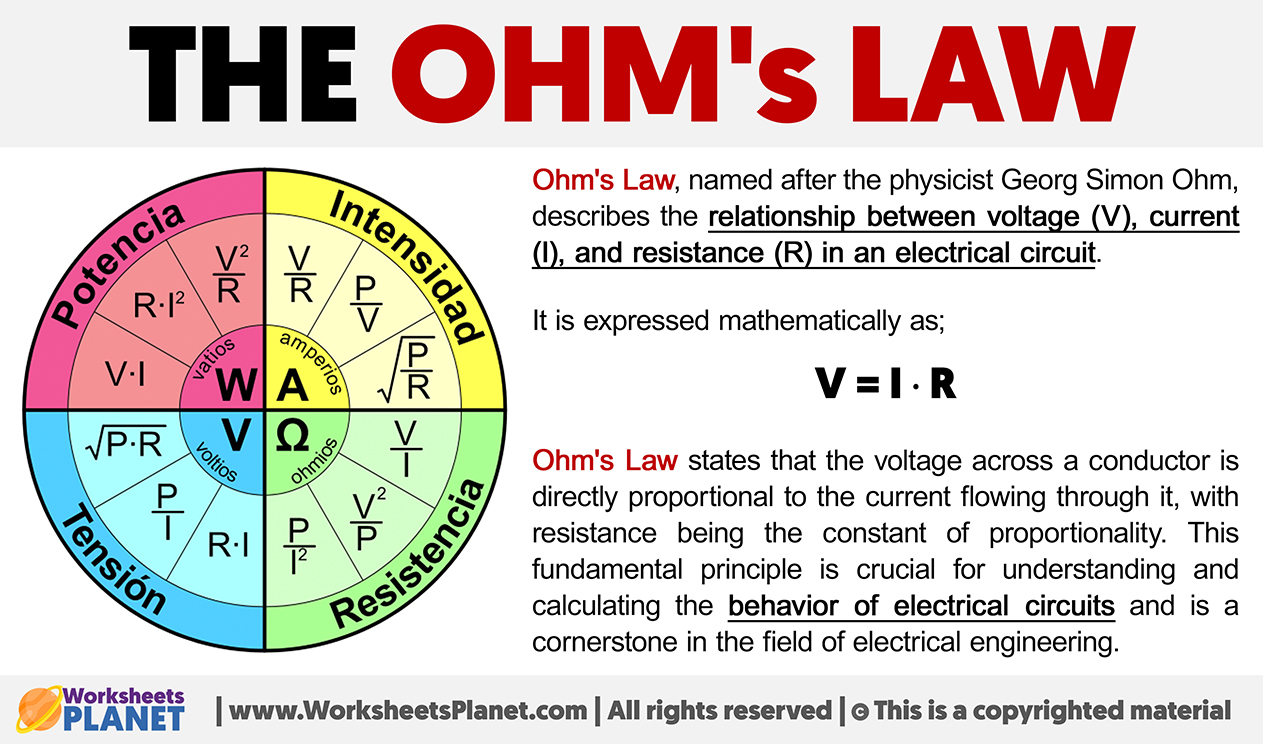
Ohm’s Law, named after the physicist Georg Simon Ohm, describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit.
It is expressed mathematically as;
V = I ∙ R
Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, with resistance being the constant of proportionality. This fundamental principle is crucial for understanding and calculating the behavior of electrical circuits and is a cornerstone in the field of electrical engineering.