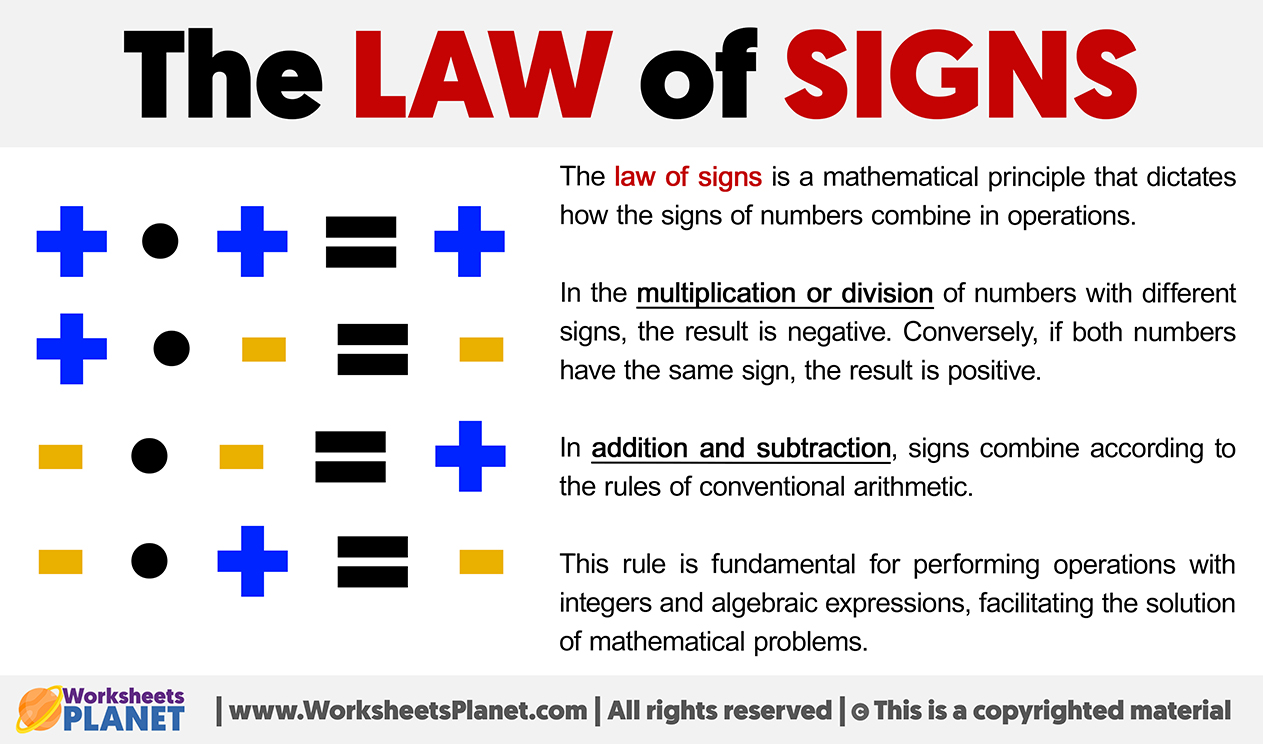
The law of signs is a mathematical principle that dictates how the signs of numbers combine in operations.
In the multiplication or division of numbers with different signs, the result is negative. Conversely, if both numbers have the same sign, the result is positive.
In addition and subtraction, signs combine according to the rules of conventional arithmetic.
This rule is fundamental for performing operations with integers and algebraic expressions, facilitating the solution of mathematical problems.