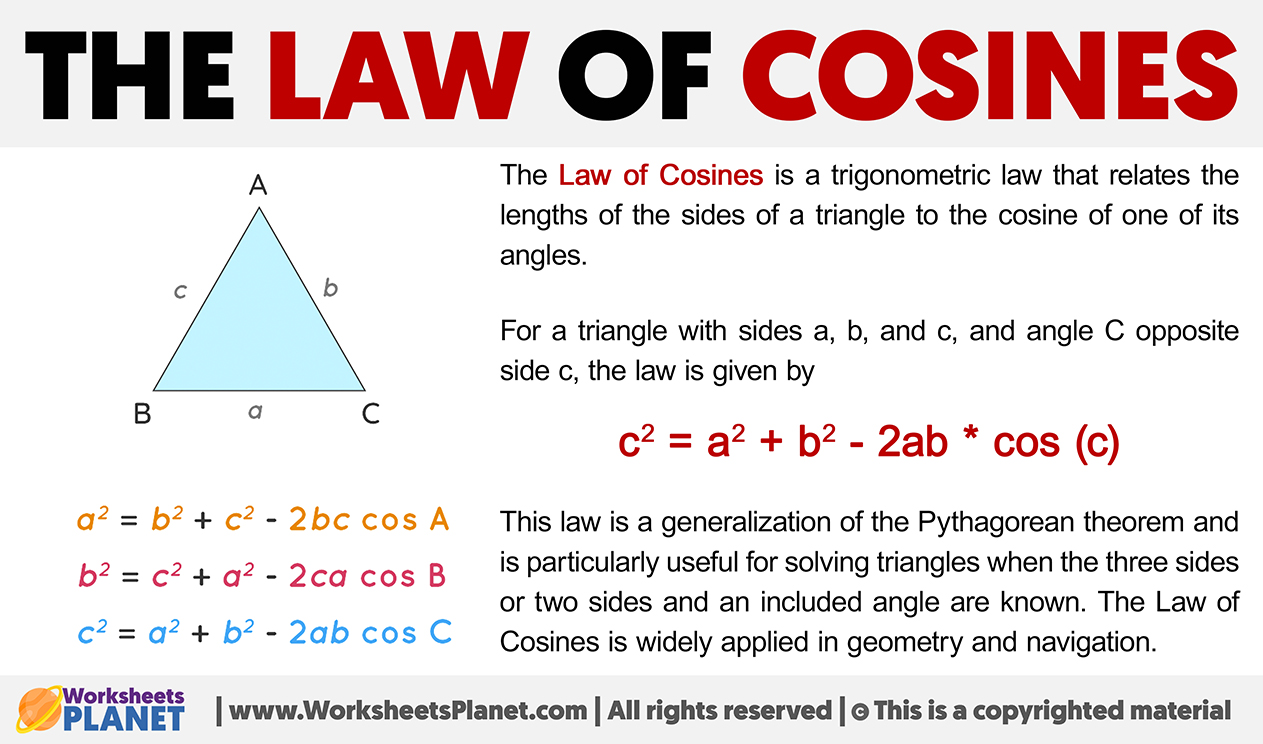
The Law of Cosines is a trigonometric law that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles.
For a triangle with sides a, b, and c, and angle C opposite side c, the law is given by
c2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab * cos (c)
This law is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem and is particularly useful for solving triangles when the three sides or two sides and an included angle are known. The Law of Cosines is widely applied in geometry and navigation.