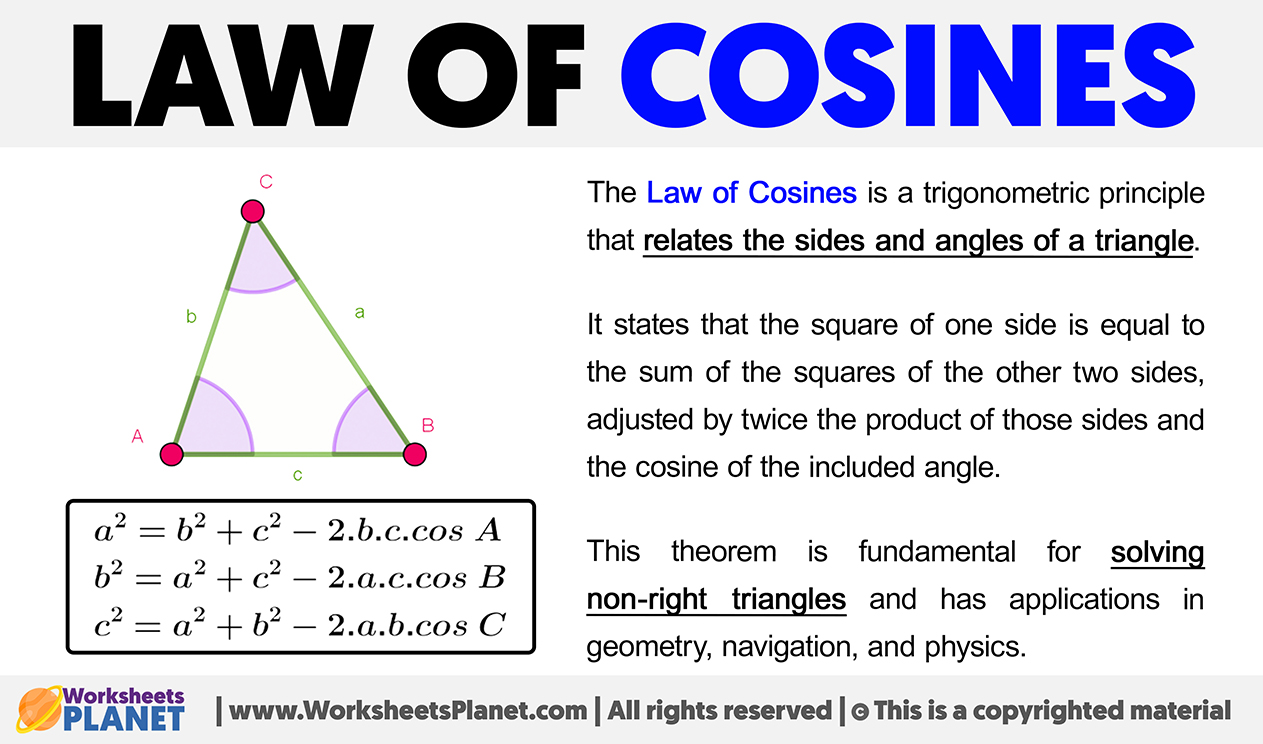
The Law of Cosines is a trigonometric principle that relates the sides and angles of a triangle.
It states that the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, adjusted by twice the product of those sides and the cosine of the included angle.
This theorem is fundamental for solving non-right triangles and has applications in geometry, navigation, and physics.