A decomposition reaction is a chemical process where a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. It often requires the input of energy, such as heat or light.
Decomposition reactions are common in various natural and industrial processes, contributing to the breakdown of complex molecules into their constituent elements or simpler compounds.
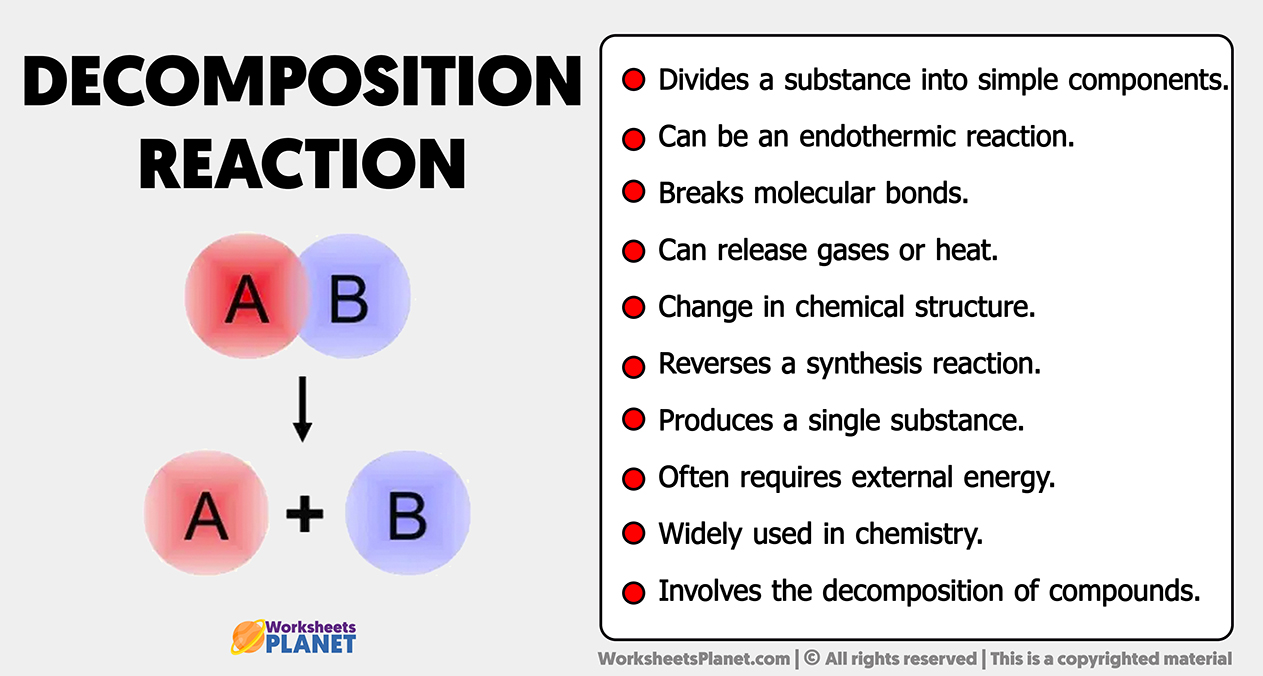
- Divides a substance into simple components.
- Can be an endothermic reaction.
- Breaks molecular bonds.
- Can release gases or heat.
- Change in chemical structure.
- Reverses a synthesis reaction.
- Produces a single substance.
- Often requires external energy.
- Widely used in chemistry.
- Involves the decomposition of compounds.

