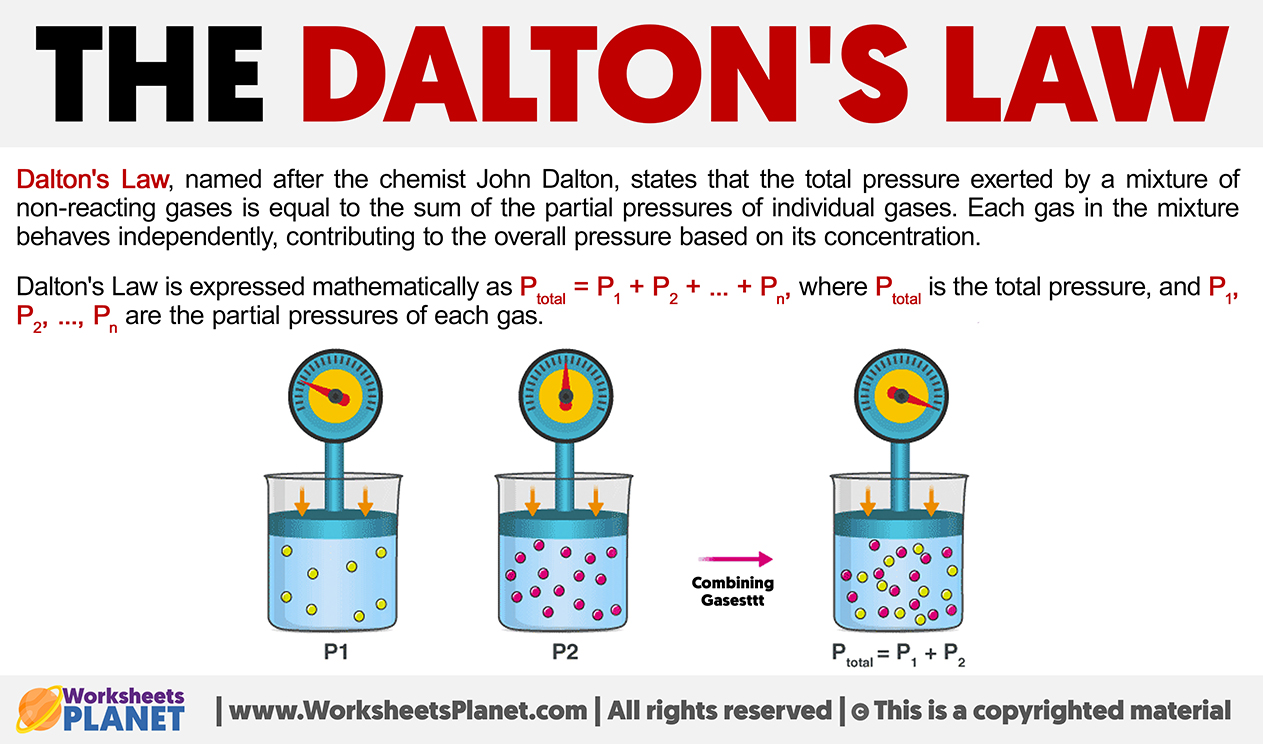
Dalton’s Law, named after the chemist John Dalton, states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of non-reacting gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of individual gases.
Each gas in the mixture behaves independently, contributing to the overall pressure based on its concentration.
Dalton’s Law is expressed mathematically as:
Ptotal = P1 + P2 + … + Pn
where Ptotal is the total pressure, and P1, P2, …, Pn are the partial pressures of each gas.