A prokaryotic cell is a simple, single-celled organism lacking a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Its genetic material is typically a singular, circular DNA molecule in the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotes, such as bacteria and archaea, perform essential life functions like metabolism and reproduction but lack the complexity seen in eukaryotic cells.
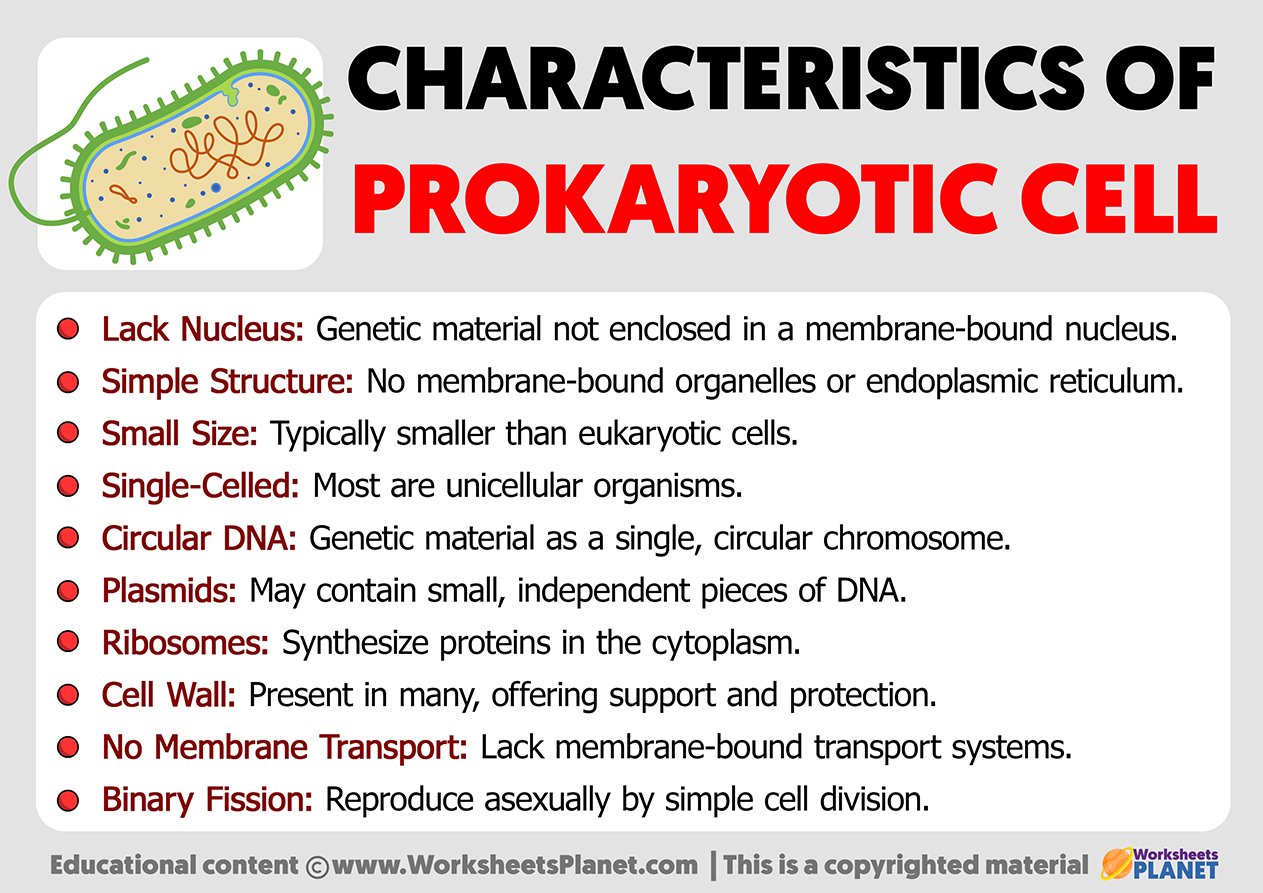
- Lack Nucleus: Genetic material not enclosed in a membrane-bound nucleus.
- Simple Structure: No membrane-bound organelles or endoplasmic reticulum.
- Small Size: Typically smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- Single-Celled: Most are unicellular organisms.
- Circular DNA: Genetic material as a single, circular chromosome.
- Plasmids: May contain small, independent pieces of DNA.
- Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins in the cytoplasm.
- Cell Wall: Present in many, offering support and protection.
- No Membrane Transport: Lack membrane-bound transport systems.
- Binary Fission: Reproduce asexually by simple cell division.

