The atomic number is one of the most relevant parts of the chemical elements that form the periodic table. The atomic number gives us information about the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus of a specific chemical element. This number is placed as a subscript, just at the top left of where the symbol of the corresponding element is located.
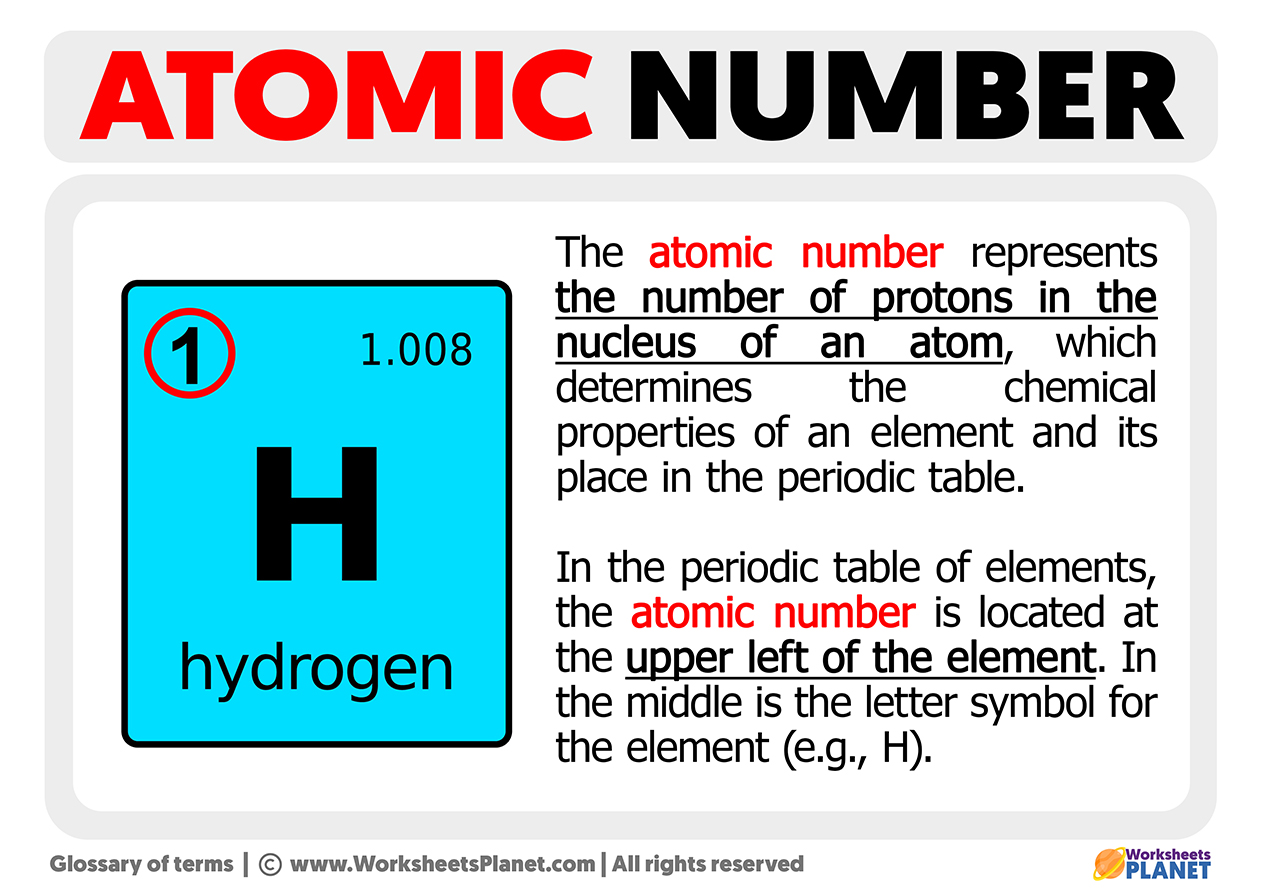
In the periodic table of elements, the atomic number is located at the upper left of the element. In the middle is the letter symbol for the element (e.g., H).
For the example on the picture above, we have chosen a hydrogen atom. For this element, all hydrogen atoms have a single proton. Therefore its atomic number, represented by the letter “Z,” is 1. Therefore, Z=1

