In this post, we’ll explain how to calculate an acute triangle’s area and show you some examples of calculating the area of an acute triangle.
The formula for the area of an acute triangle
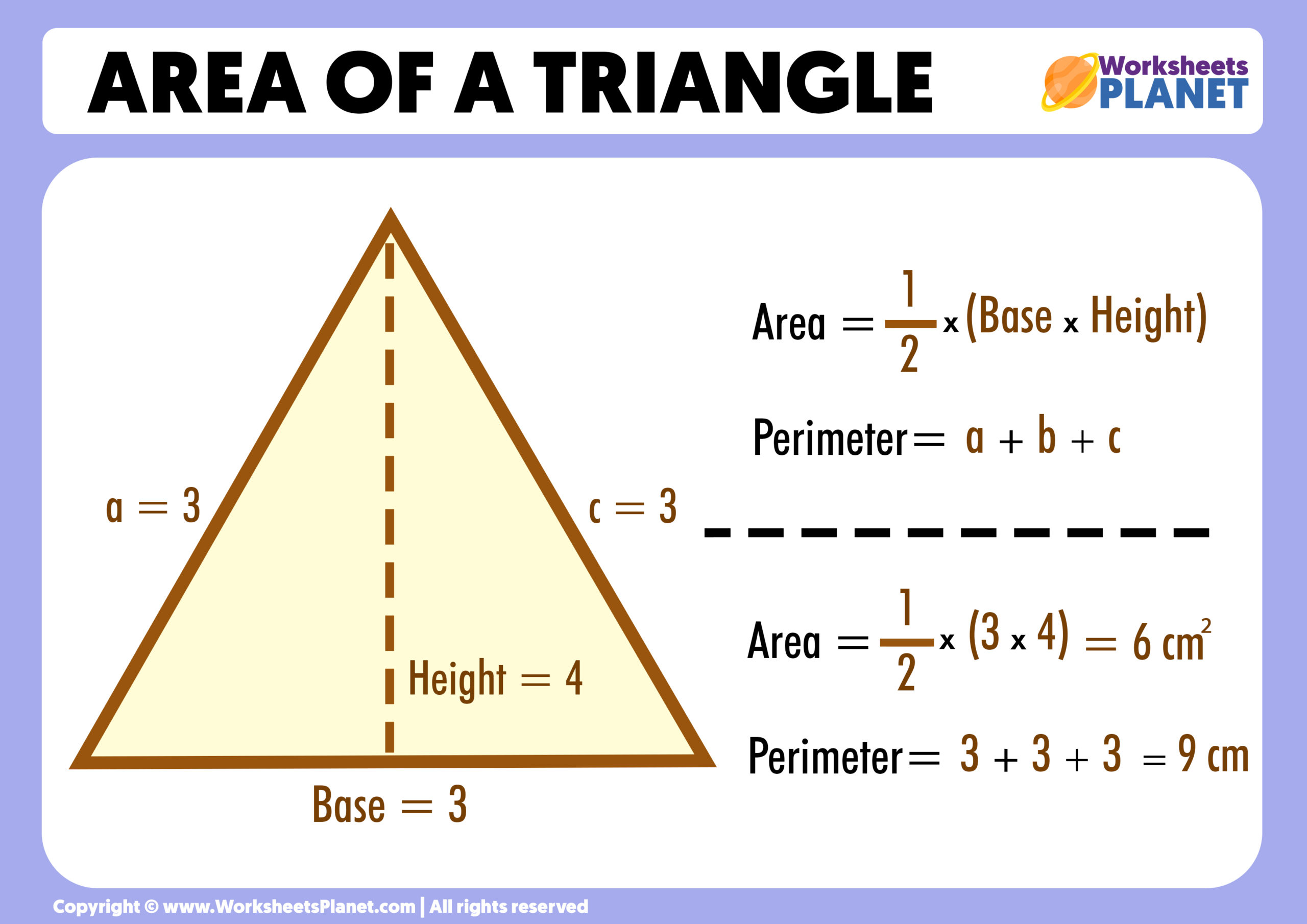
The area of an acute triangle is equal to the product of the base of the acute triangle and its height divided by two.
Therefore, to find the area of an acute triangle, you must first find the triangle’s height, then multiply that height by the length of the base of the triangle. In summary, the formula to calculate the area of an acute triangle is as follows:
You should keep in mind that there are three types of acute triangles:
- Equilateral triangle: the three sides of the acute triangle are equal, and its three internal angles are 60º.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides of the acute triangle are equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides of the acute triangle are different.
However, we must use the same formula to find the area of the acute triangle, no matter what type.

