Hey Teachers! Here you have new resource for your class. This totally free material is made up of 8 different slides that will help you explaining what volcanoes are to your students. Appart from the theory slides, you’ll find a template to build your own volcano mock-up. Your students will love the mock-up!!

What is a volcano?
A volcano is a type of mountain that emerges from the earth’s crust through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape. A volcano becomes active when it erupts. An eruption is when lava and gas are released from a volcano. Volcanoes emit rocks that can reach 4-200 kilometres high. Volcanoes also emit lava which can reach temperatures between 700-1,300° celsius.
What is the origin of volcano?
The word “volcano” comes from an island in Italy called “Vulcano”; a volcanic island in Sicily. Roman mythology says that Vulcan, god of fire and volcanoes, called this island “Vulcano”. Legend says if the Romans made him angry, the volcano would erupt.
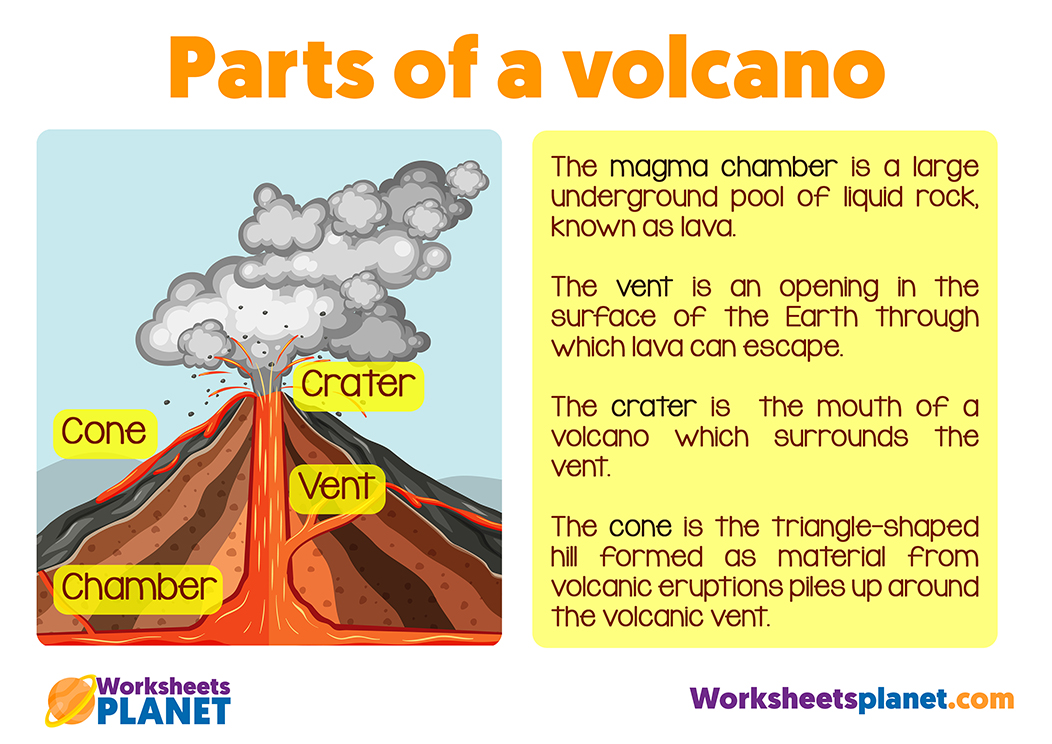
What are the parts of a volcano?
The magma chamber is a large underground pool of liquid rock, known as lava. The vent is an opening in the surface of the Earth through which lava can escape. The crater is the mouth of a volcano which surrounds the vent. The cone is the triangle-shaped hill formed as material from volcanic eruptions piles up around the volcanic vent.
How do volcanoes erupt?
A volcanic eruption takes place when magma’s temperature get very high under the Earth’s surface. When magma reaches extreme temperatures; lava, rocks, dust, and gas from the Earth’s interior are thrown out of the volcano. There are different types of eruptions that define the type of volcano. Volcanic eruptions may fall into six major types: Icelandic, Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, Pelean, and Plinian.
How does magma form?
Magma is molten rock mixed with gas found under the Earth’s surface. Lava is the liquid that emerges from the Earth’s surface during a volcanic eruption. When the lava cools down, it forms solid rocks, such as diorite, basalt or granite. Then, it starts the rock cycle, where solid rocks suffer different changes until they become magma again.
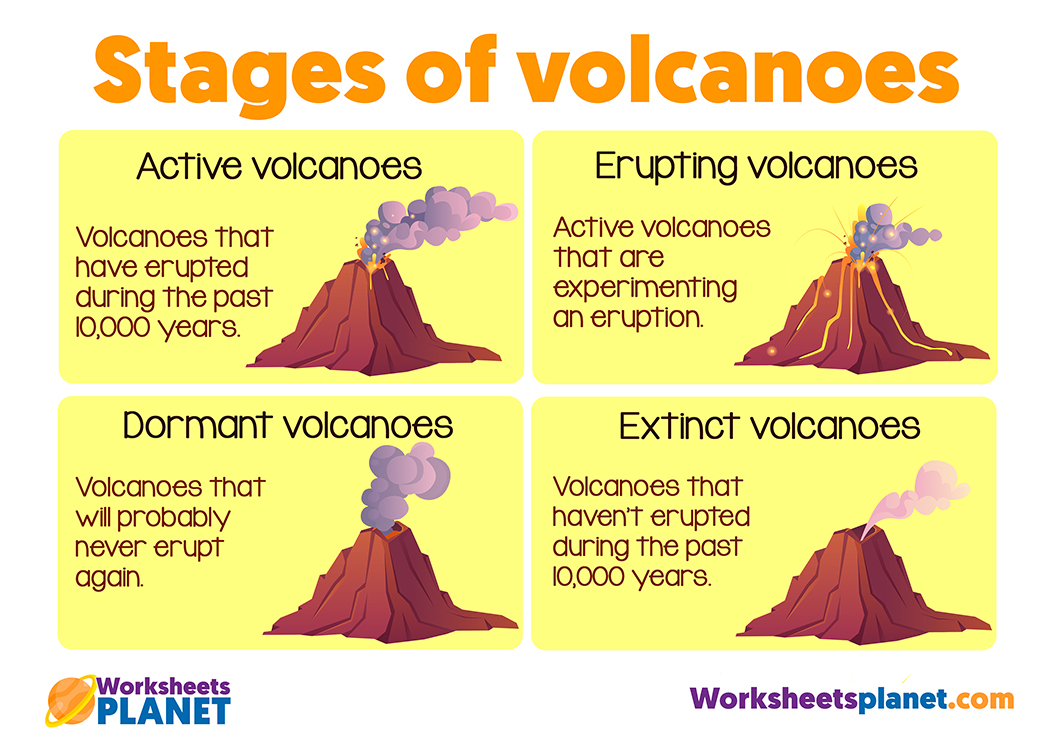
What are the stages of a volcano?
- Active volcanoes: volcanoes that have erupted during the past 10,000 years.
- Erupting volcanoes: active volcanoes that are experimenting an eruption.
- Dormant volcanoes: volcanoes that will probably never erupt again.
- Extinct volcanoes: volcanoes that haven’t erupted during the past 10,000 years.
What is the science of studying volcanoes?
Volcanology is a young and exciting career that deals with the study of one of the earth’s most dynamic processes: volcanoes. It also studies geysers, volcanic gases, magma, lava or tephra. A volcanologist is a geologist who studies the eruptive activity and formation of volcanoes and their current and historic eruptions. They usually visit erupting volcanoes to observe this process and to collect samples, such as tephra.