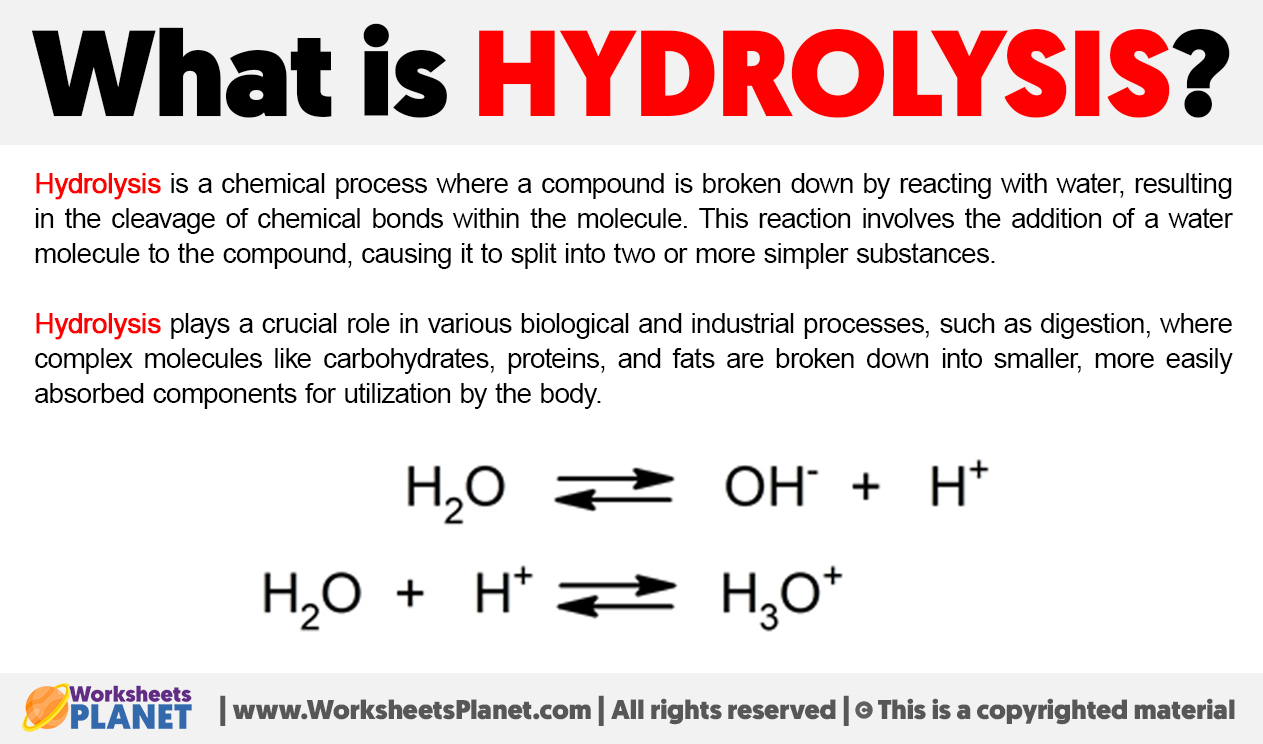
Hydrolysis is a chemical process where a compound is broken down by reacting with water, resulting in the cleavage of chemical bonds within the molecule.
This reaction involves the addition of a water molecule to the compound, causing it to split into two or more simpler substances.
Hydrolysis plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes, such as digestion, where complex molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are broken down into smaller, more easily absorbed components for utilization by the body.