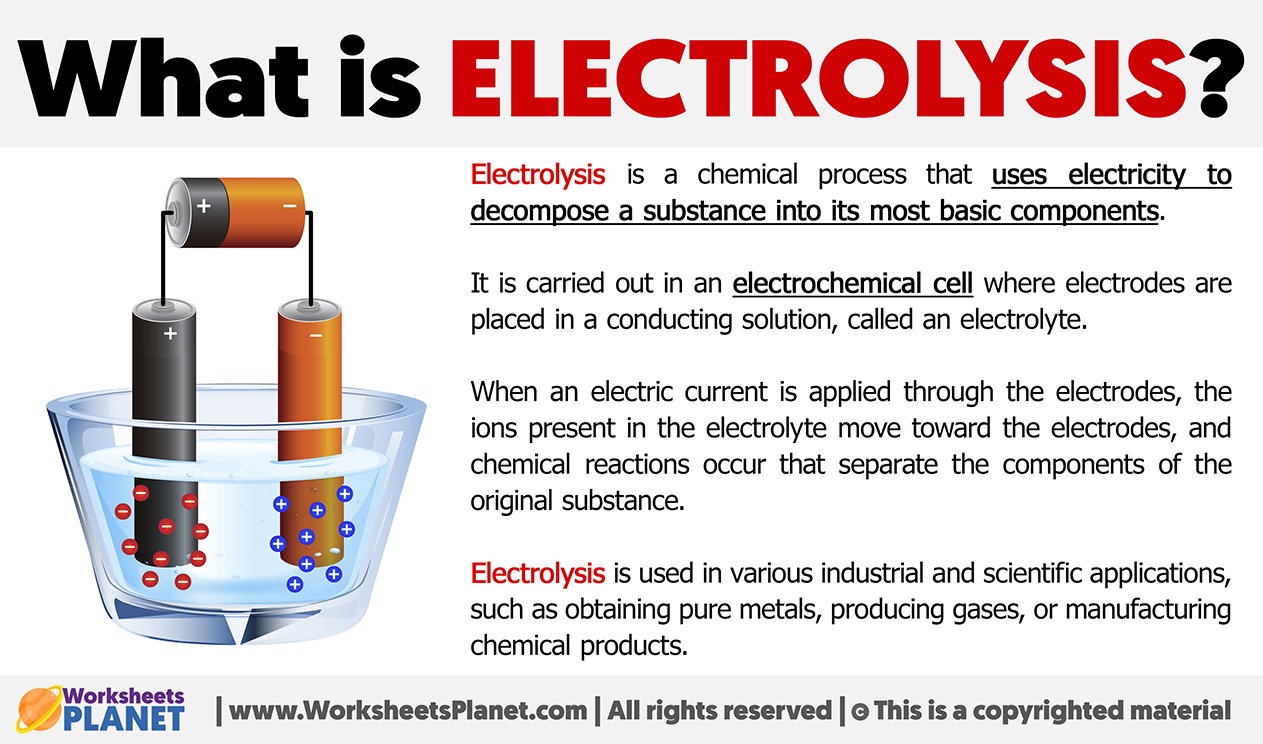
Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses electricity to decompose a substance into its most basic components.
It is carried out in an electrochemical cell where electrodes are placed in a conducting solution, called an electrolyte.
When an electric current is applied through the electrodes, the ions present in the electrolyte move toward the electrodes, and chemical reactions occur that separate the components of the original substance.
Electrolysis is used in various industrial and scientific applications, such as obtaining pure metals, producing gases, or manufacturing chemical products.