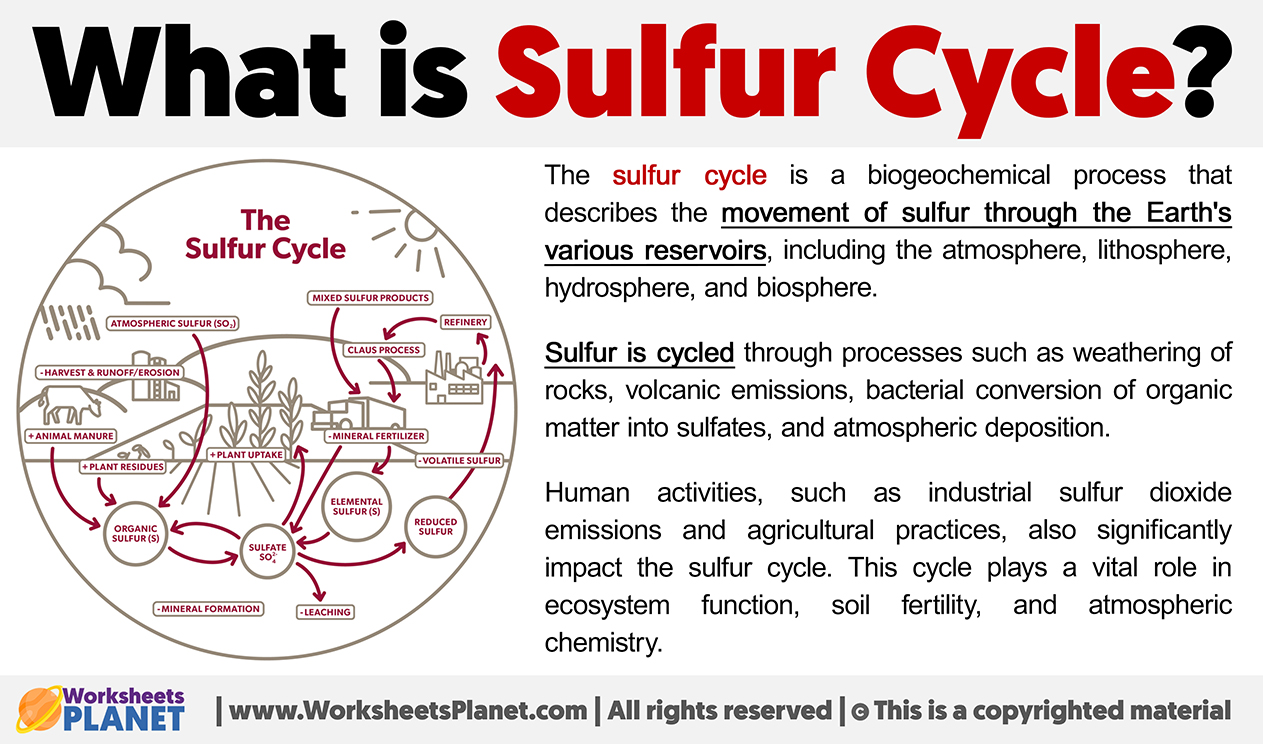
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical process that describes the movement of sulfur through the Earth’s various reservoirs, including the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Sulfur is cycled through processes such as weathering of rocks, volcanic emissions, bacterial conversion of organic matter into sulfates, and atmospheric deposition.
Human activities, such as industrial sulfur dioxide emissions and agricultural practices, also significantly impact the sulfur cycle. This cycle plays a vital role in ecosystem function, soil fertility, and atmospheric chemistry.