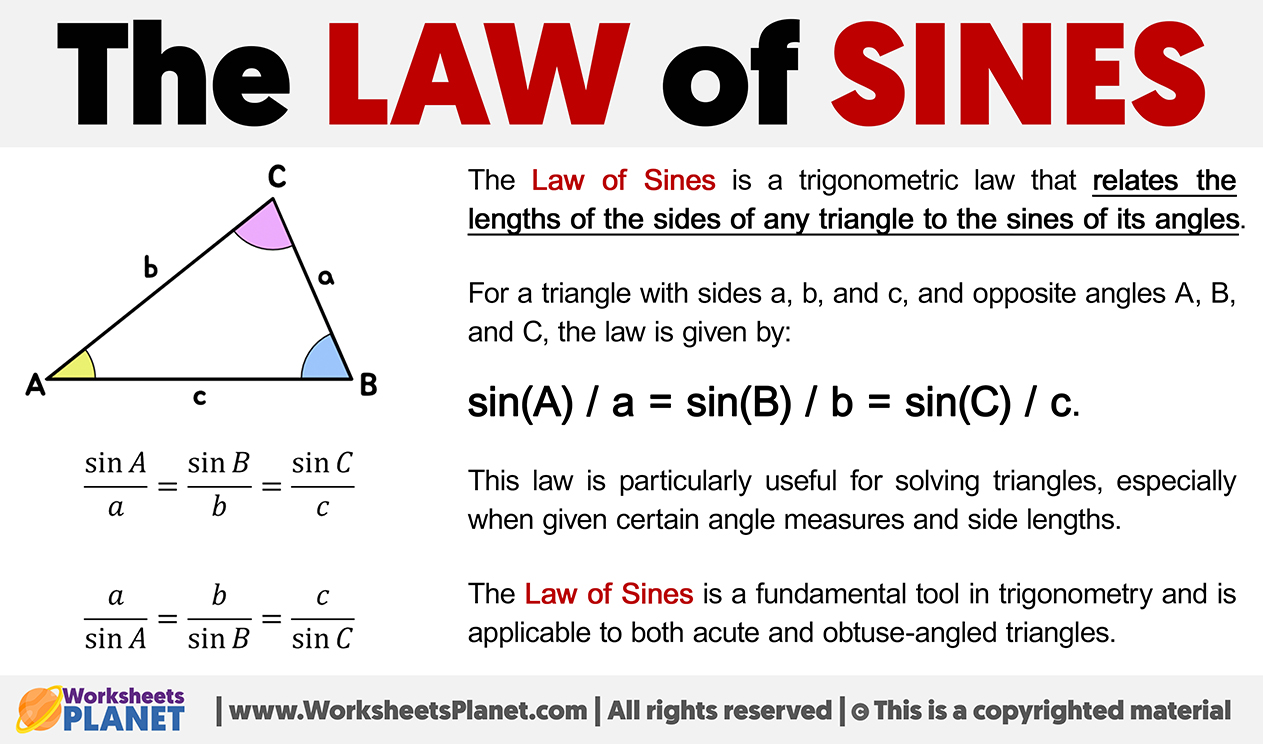
The Law of Sines is a trigonometric law that relates the lengths of the sides of any triangle to the sines of its angles.
For a triangle with sides a, b, and c, and opposite angles A, B, and C, the law is given by:
sin(A) / a = sin(B) / b = sin(C) / c.
This law is particularly useful for solving triangles, especially when given certain angle measures and side lengths. The Law of Sines is a fundamental tool in trigonometry and is applicable to both acute and obtuse-angled triangles.