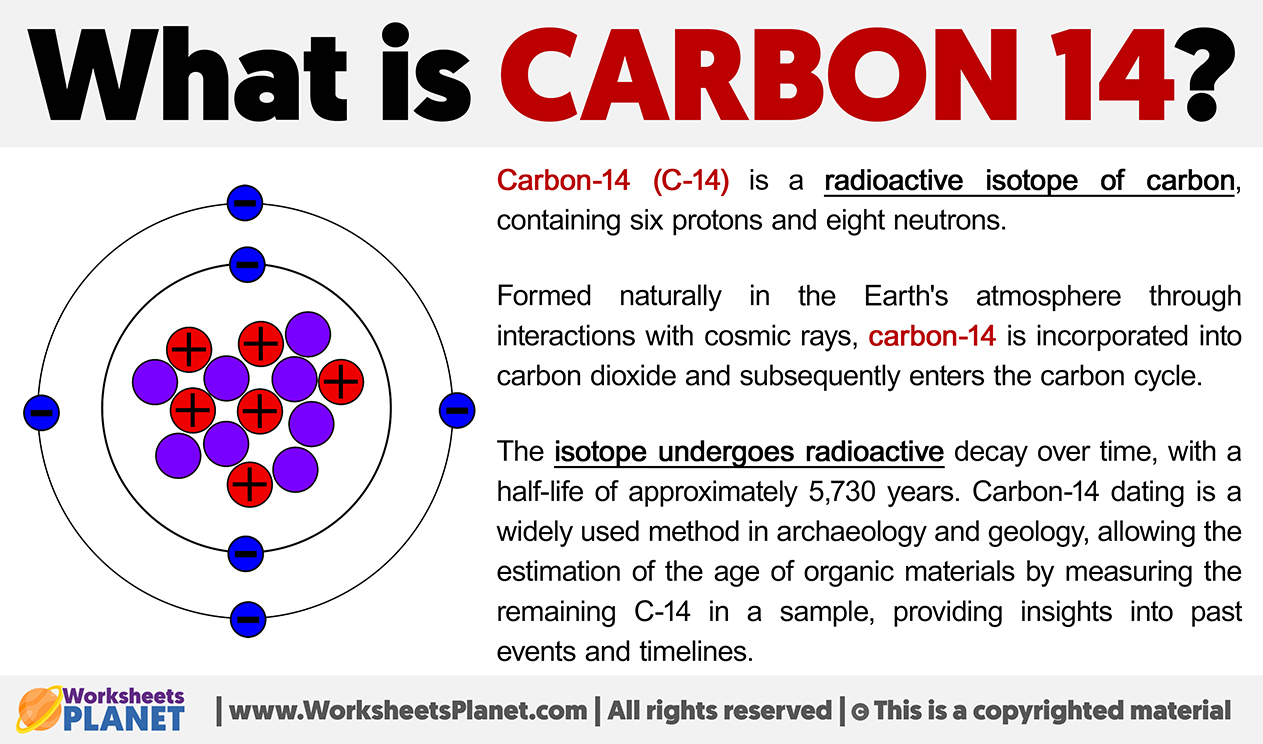
Carbon-14 (C-14) is a radioactive isotope of carbon, containing six protons and eight neutrons. Formed naturally in the Earth’s atmosphere through interactions with cosmic rays, carbon-14 is incorporated into carbon dioxide and subsequently enters the carbon cycle.
The isotope undergoes radioactive decay over time, with a half-life of approximately 5,730 years. Carbon-14 dating is a widely used method in archaeology and geology, allowing the estimation of the age of organic materials by measuring the remaining C-14 in a sample, providing insights into past events and timelines.