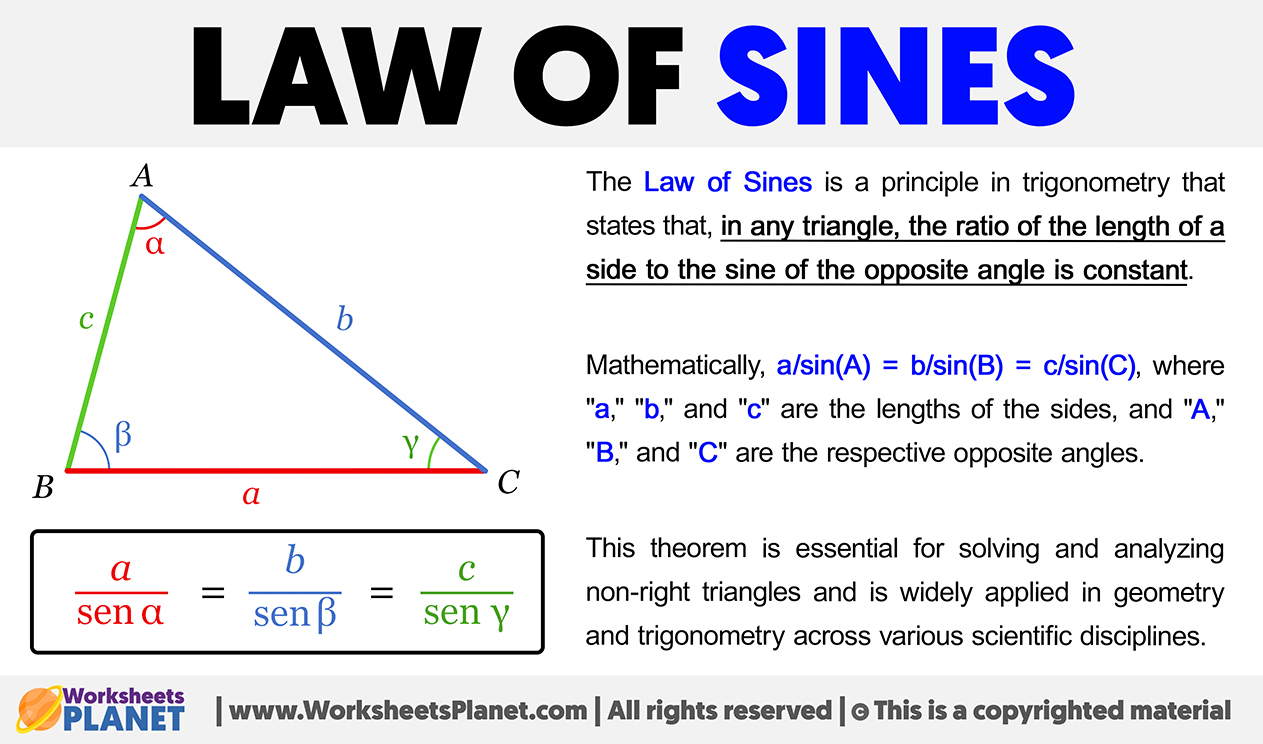
The Law of Sines is a principle in trigonometry that states that, in any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of the opposite angle is constant.
Mathematically:
a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C)
where “a,” “b,” and “c” are the lengths of the sides, and “A,” “B,” and “C” are the respective opposite angles.
This theorem is essential for solving and analyzing non-right triangles and is widely applied in geometry and trigonometry across various scientific disciplines.