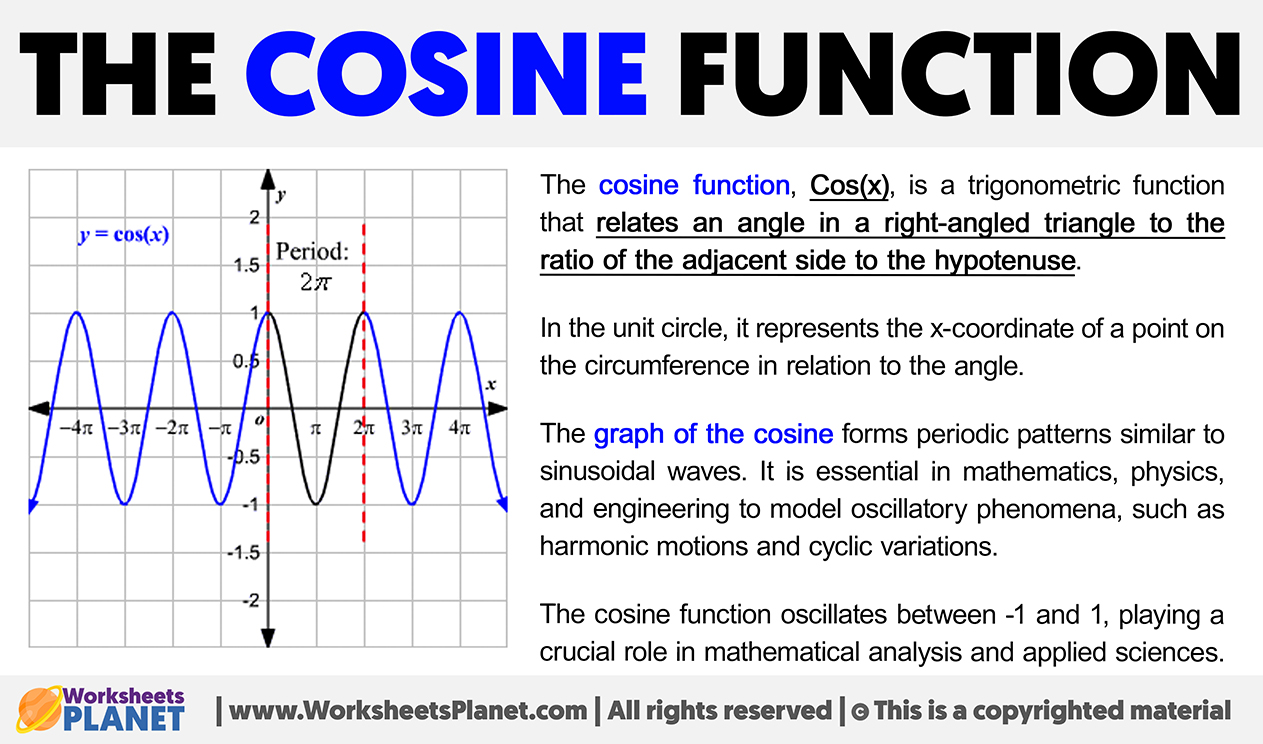
The cosine function, Cos(x), is a trigonometric function that relates an angle in a right-angled triangle to the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse.
In the unit circle, it represents the x-coordinate of a point on the circumference in relation to the angle. The graph of the cosine forms periodic patterns similar to sinusoidal waves. It is essential in mathematics, physics, and engineering to model oscillatory phenomena, such as harmonic motions and cyclic variations.
The cosine function oscillates between -1 and 1, playing a crucial role in mathematical analysis and applied sciences.