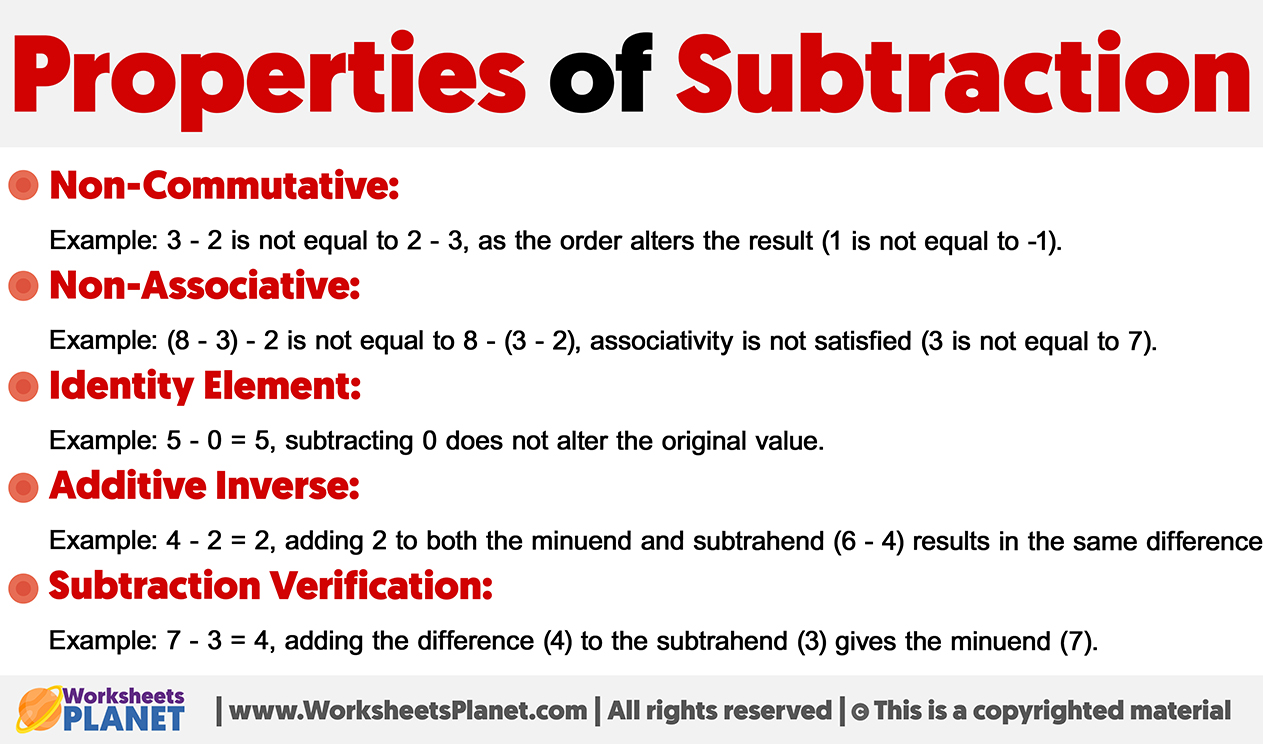
Non-Commutative:
Example: 3 – 2 is not equal to 2 – 3, as the order alters the result (1 is not equal to -1).
Non-Associative:
Example: (8 – 3) – 2 is not equal to 8 – (3 – 2), associativity is not satisfied (3 is not equal to 7).
Identity Element:
Example: 5 – 0 = 5, subtracting 0 does not alter the original value.
Additive Inverse:
Example: 4 – 2 = 2, adding 2 to both the minuend and subtrahend (6 – 4) results in the same difference.
Subtraction Verification:
Example: 7 – 3 = 4, adding the difference (4) to the subtrahend (3) gives the minuend (7).