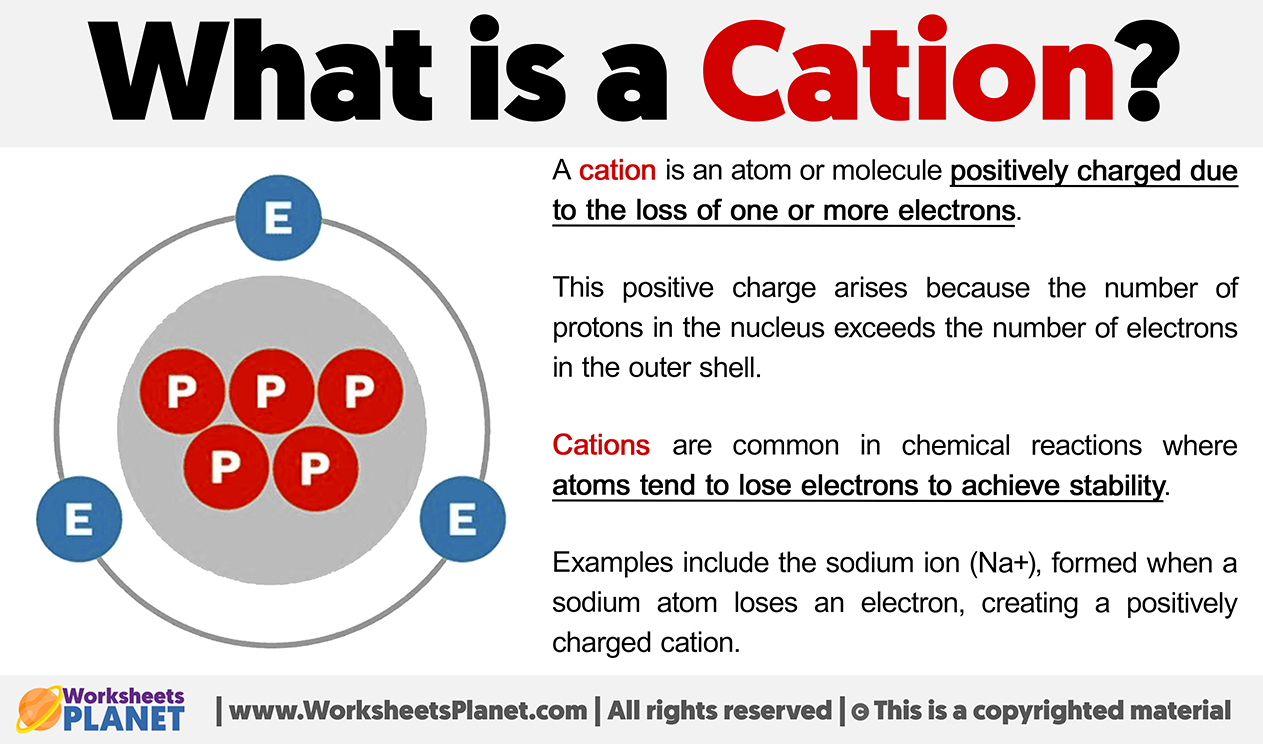
A cation is an atom or molecule positively charged due to the loss of one or more electrons. This positive charge arises because the number of protons in the nucleus exceeds the number of electrons in the outer shell.
Cations are common in chemical reactions where atoms tend to lose electrons to achieve stability.
Examples include the sodium ion (Na+), formed when a sodium atom loses an electron, creating a positively charged cation.