The water cycle is a natural process that describes the continuous movement of water on Earth.
It involves several stages: evaporation, where water transforms from liquid to vapor; condensation, as vapor forms clouds; precipitation, when water falls back to Earth as rain, snow, or other forms; and runoff, where water flows into rivers and oceans, restarting the cycle.
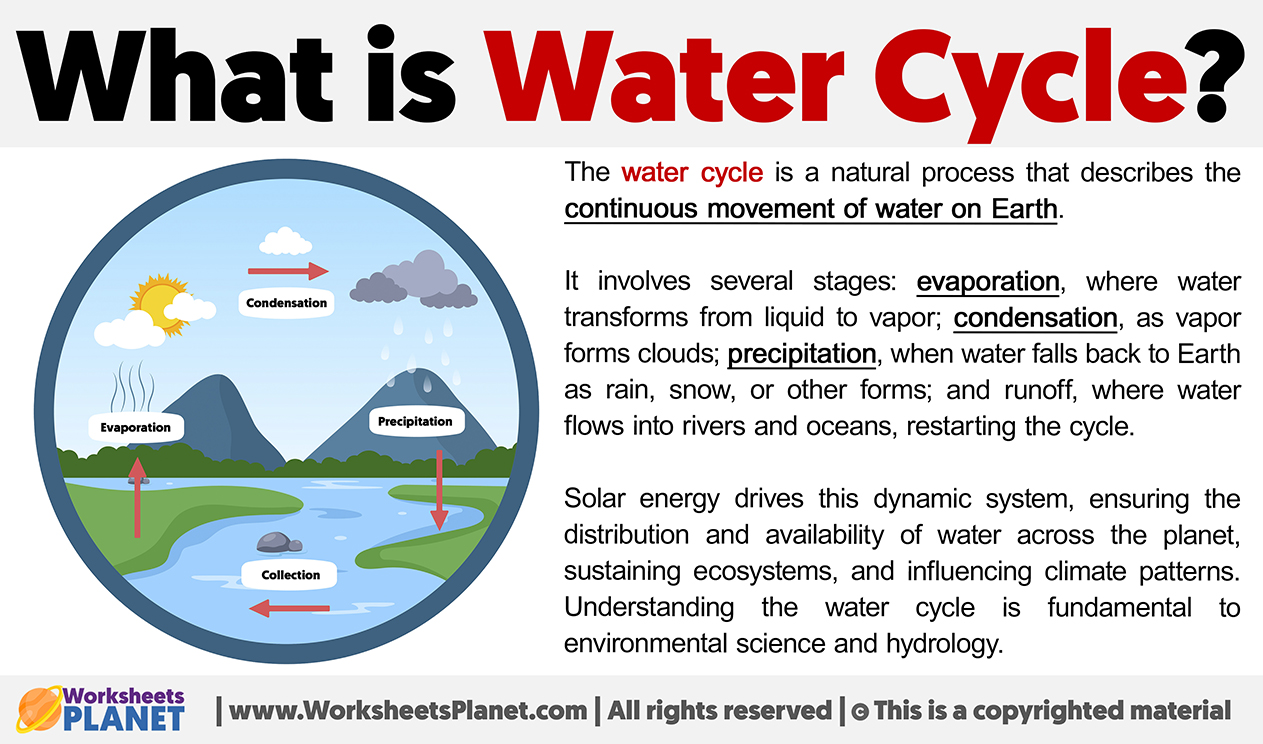
Solar energy drives this dynamic system, ensuring the distribution and availability of water across the planet, sustaining ecosystems, and influencing climate patterns. Understanding the water cycle is fundamental to environmental science and hydrology.

