An electron is a subatomic particle with a negative charge that orbits the nucleus of an atom. It plays a crucial role in chemical reactions and electrical conductivity.
Electrons have a negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons and are involved in the formation of chemical bonds between atoms. Manipulating electron behavior is central to various technologies, including electronics.
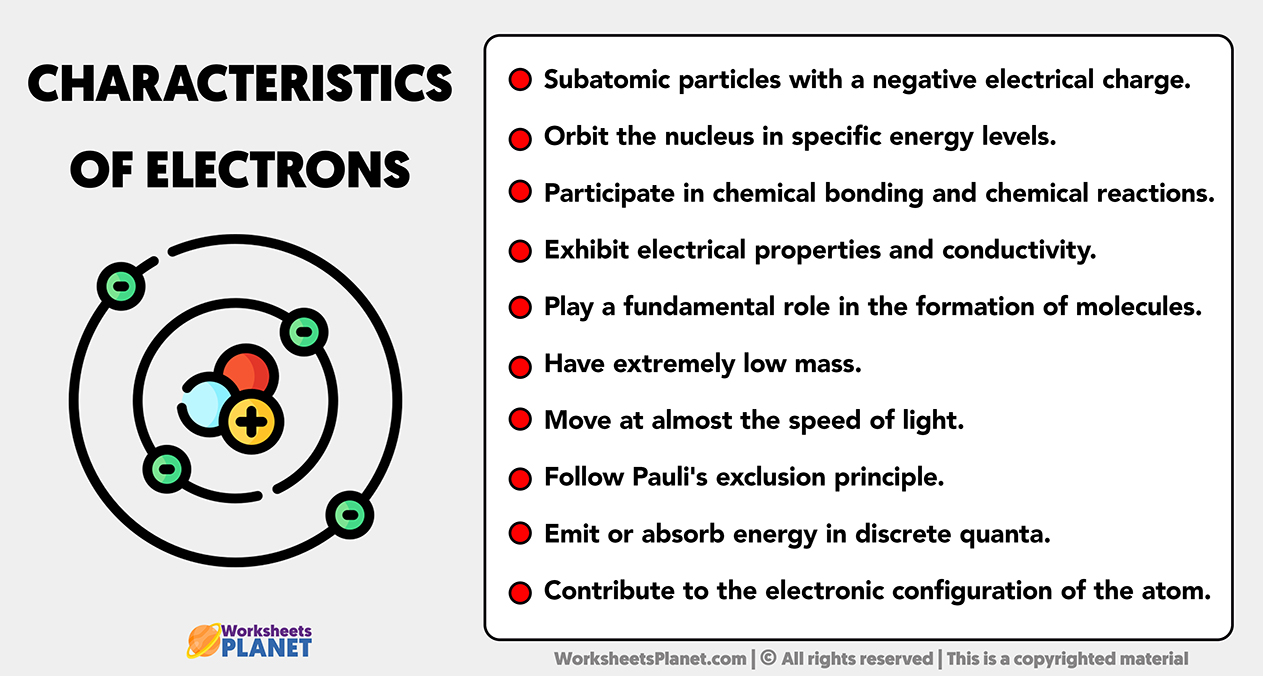
Main Characteristics of Electrons
- Subatomic particles with a negative electrical charge.
- Orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels.
- Participate in chemical bonding and chemical reactions.
- Exhibit electrical properties and conductivity.
- Play a fundamental role in the formation of molecules.
- Have extremely low mass.
- Move at almost the speed of light.
- Follow Pauli’s exclusion principle.
- Emit or absorb energy in discrete quanta.
- Contribute to the electronic configuration of the atom.

