Viruses are microscopic infectious agents composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat. They lack cellular structures and can only replicate inside living host cells, hijacking the cell’s machinery to reproduce.
Viruses cause various diseases in humans, animals, and plants and play a crucial role in ecology and disease transmission.
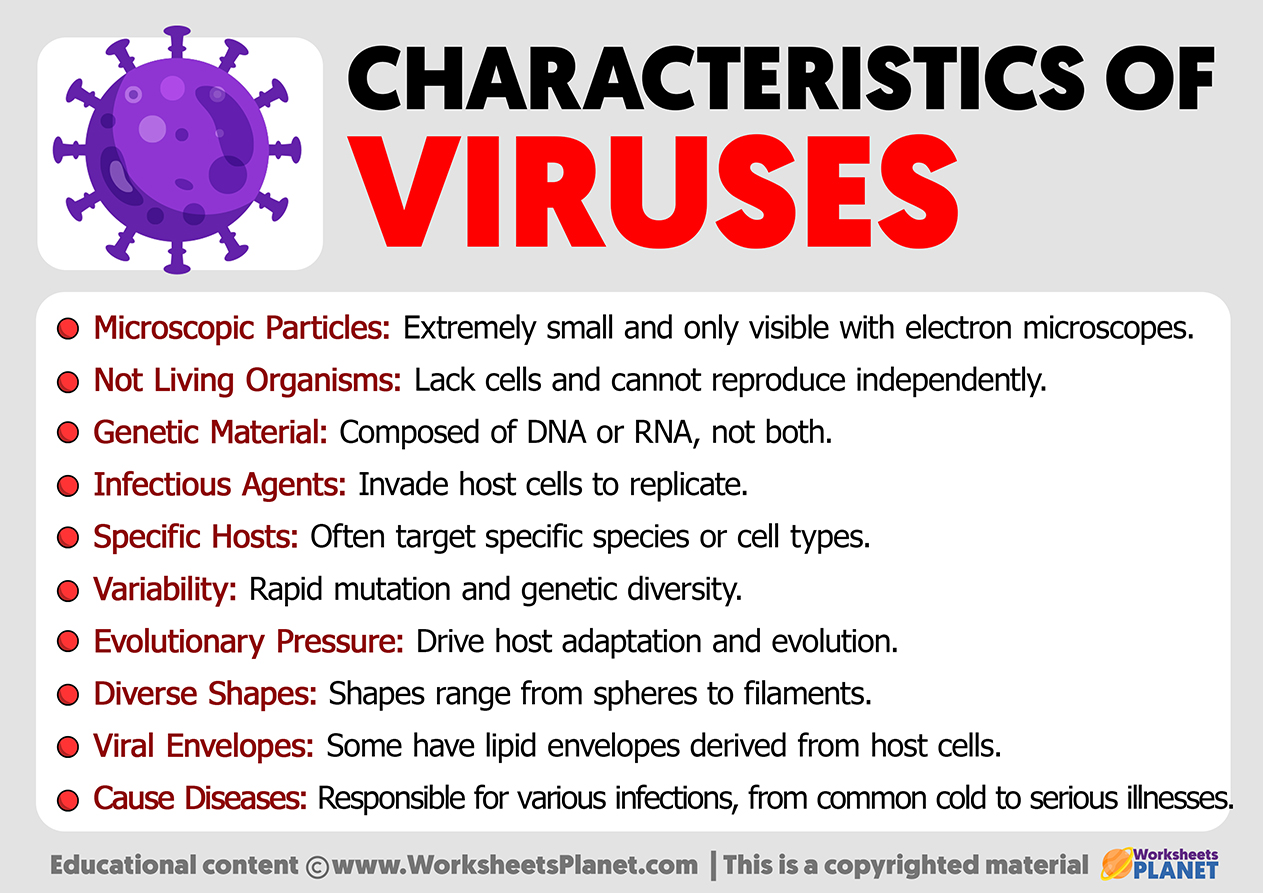
- Microscopic Particles: Extremely small and only visible with electron microscopes.
- Not Living Organisms: Lack cells and cannot reproduce independently.
- Genetic Material: Composed of DNA or RNA, not both.
- Infectious Agents: Invade host cells to replicate.
- Specific Hosts: Often target specific species or cell types.
- Variability: Rapid mutation and genetic diversity.
- Evolutionary Pressure: Drive host adaptation and evolution.
- Diverse Shapes: Shapes range from spheres to filaments.
- Viral Envelopes: Some have lipid envelopes derived from host cells.
- Cause Diseases: Responsible for various infections, from common cold to serious illnesses.

